OCI Kubernetes Engine (OKE) Terraform Module
Introduction
This module automates the provisioning of an OKE cluster.
The documentation here is for 5.x only. The documentation for earlier versions can be found on the GitHub repo on the relevant branch.
News
December 4, 2024: Announcing v5.2.2
- feat: add support to reference module nsgs in the nsg rules
November 18, 2024: Announcing v5.2.1
- fix: operator custom cloud-init error by @mcouto-sossego in #950
- feat: added rules to allow UDP to be used for node port ranges by @robo-cap in #961
November 7, 2024: Announcing v5.2.0
- Add support for stateless rules
- Fix KMS policy - cluster dependency
- Add cluster addon support
- Allow cloud-init update for nodepools
- Add several improvements and fixes
- Cilium extension upgrade to 1.16
- Fix pod nsg bug
July 9, 2024: Announcing v5.1.8
- allow user to add additional rules to the workers NSG
- docs: updated main page, mdbook component versions
- Add support to ignore_initial_pool_size attribute on nodepools
May 9 2023: Announcing release v4.5.9
- Make the default freeform_tags empty
- Use lower bound version specification for oci provider
Related Documentation
- VCN Module Documentation
- Bastion Module Documentation
- Operator Module Documentation
- DRG Module Documentation
Changelog
View the CHANGELOG.
Security
Please consult the security guide for our responsible security vulnerability disclosure process
License
Copyright (c) 2019-2023 Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Released under the Universal Permissive License v1.0 as shown at https://oss.oracle.com/licenses/upl/.
Getting started
This module automates the provisioning of an OKE cluster.
The documentation here is for 5.x only. The documentation for earlier versions can be found on the GitHub repo.
Usage
Clone the repo
Clone the git repo:
git clone https://github.com/oracle-terraform-modules/terraform-oci-oke.git tfoke
cd tfoke
Create
- Create 2 OCI providers and add them to providers.tf:
provider "oci" {
fingerprint = var.api_fingerprint
private_key_path = var.api_private_key_path
region = var.region
tenancy_ocid = var.tenancy_id
user_ocid = var.user_id
}
provider "oci" {
fingerprint = var.api_fingerprint
private_key_path = var.api_private_key_path
region = var.home_region
tenancy_ocid = var.tenancy_id
user_ocid = var.user_id
alias = "home"
}
- Initialize a working directory containing Terraform configuration files, and optionally upgrade module dependencies:
terraform init --upgrade
- Create a terraform.tfvars and provide the necessary parameters:
# Identity and access parameters
api_fingerprint = "00:ab:12:34:56:cd:78:90:12:34:e5:fa:67:89:0b:1c"
api_private_key_path = "~/.oci/oci_rsa.pem"
home_region = "us-ashburn-1"
region = "ap-sydney-1"
tenancy_id = "ocid1.tenancy.oc1.."
user_id = "ocid1.user.oc1.."
# general oci parameters
compartment_id = "ocid1.compartment.oc1.."
timezone = "Australia/Sydney"
# ssh keys
ssh_private_key_path = "~/.ssh/id_ed25519"
ssh_public_key_path = "~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub"
# networking
create_vcn = true
assign_dns = true
lockdown_default_seclist = true
vcn_cidrs = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
vcn_dns_label = "oke"
vcn_name = "oke"
# Subnets
subnets = {
bastion = { newbits = 13, netnum = 0, dns_label = "bastion", create="always" }
operator = { newbits = 13, netnum = 1, dns_label = "operator", create="always" }
cp = { newbits = 13, netnum = 2, dns_label = "cp", create="always" }
int_lb = { newbits = 11, netnum = 16, dns_label = "ilb", create="always" }
pub_lb = { newbits = 11, netnum = 17, dns_label = "plb", create="always" }
workers = { newbits = 2, netnum = 1, dns_label = "workers", create="always" }
pods = { newbits = 2, netnum = 2, dns_label = "pods", create="always" }
}
# bastion
create_bastion = true
bastion_allowed_cidrs = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
bastion_user = "opc"
# operator
create_operator = true
operator_install_k9s = true
# iam
create_iam_operator_policy = "always"
create_iam_resources = true
create_iam_tag_namespace = false // true/*false
create_iam_defined_tags = false // true/*false
tag_namespace = "oke"
use_defined_tags = false // true/*false
# cluster
create_cluster = true
cluster_name = "oke"
cni_type = "flannel"
kubernetes_version = "v1.29.1"
pods_cidr = "10.244.0.0/16"
services_cidr = "10.96.0.0/16"
# Worker pool defaults
worker_pool_size = 0
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
# Worker defaults
await_node_readiness = "none"
worker_pools = {
np1 = {
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 2,
memory = 32,
size = 1,
boot_volume_size = 50,
kubernetes_version = "v1.29.1"
}
np2 = {
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 2,
memory = 32,
size = 3,
boot_volume_size = 150,
kubernetes_version = "v1.29.1"
}
}
# Security
allow_node_port_access = false
allow_worker_internet_access = true
allow_worker_ssh_access = true
control_plane_allowed_cidrs = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
control_plane_is_public = false
load_balancers = "both"
preferred_load_balancer = "public"
- Run the plan and apply commands to create OKE cluster and other components:
terraform plan
terraform apply
You can create a Kubernetes cluster with the latest version of Kubernetes available in OKE using this terraform script.
Connect
NOTE: TODO Add content
kubectl is installed on the operator host by default and the kubeconfig file is set in the default location (~/.kube/config) so you don't need to set the KUBECONFIG environment variable every time you log in to the operator host.
The instance principal of the operator must be granted MANAGE on target cluster for configuration of an admin user context.
An alias "k" will be created for kubectl on the operator host.
If you would like to use kubectl locally, first install and configure OCI CLI locally. Then, install kubectl and set the KUBECONFIG to the config file path.
export KUBECONFIG=path/to/kubeconfig
To be able to get the kubeconfig file, you will need to get the credentials with terraform and store in the preferred storage format (e.g: file, vault, bucket...):
# OKE cluster creation.
module "oke_my_cluster" {
#...
}
# Obtain cluster Kubeconfig.
data "oci_containerengine_cluster_kube_config" "kube_config" {
cluster_id = module.oke_my_cluster.cluster_id
}
# Store kubeconfig in vault.
resource "vault_generic_secret" "kube_config" {
path = "my/cluster/path/kubeconfig"
data_json = jsonencode({
"data" : data.oci_containerengine_cluster_kube_config.kube_config.content
})
}
# Store kubeconfig in file.
resource "local_file" "kube_config" {
content = data.oci_containerengine_cluster_kube_config.kube_config.content
filename = "/tmp/kubeconfig"
file_permission = "0600"
}
Update
NOTE: TODO Add content
Destroy
Run the below command to destroy the infrastructure created by Terraform:
terraform destroy
You can also do targeted destroy e.g.
terraform destroy --target=module.workers
Prerequisites
This section will guide you through the prerequisites before you can use this project.
Identity and Access Management Rights
The Terraform user must have the following permissions to:
- MANAGE dynamic groups (instance_principal and KMS integration)
- MANAGE cluster-family in compartment
- MANAGE virtual-network-family in compartment
- MANAGE instance-family in compartment
Install Terraform
Start by installing Terraform and configuring your path.
Download Terraform
- Open your browser and navigate to the Terraform download page. You need version 1.0.0+.
- Download the appropriate version for your operating system
- Extract the the contents of compressed file and copy the terraform binary to a location that is in your path (see next section below)
Configure path on Linux/macOS
Open a terminal and enter the following:
# edit your desired path in-place:
sudo mv /path/to/terraform /usr/local/bin
Configure path on Windows
Follow the steps below to configure your path on Windows:
- Click on 'Start', type 'Control Panel' and open it
- Select System > Advanced System Settings > Environment Variables
- Select System variables > PATH and click 'Edit'
- Click New and paste the location of the directory where you have extracted the terraform.exe
- Close all open windows by clicking OK
- Open a new terminal and verify terraform has been properly installed
Testing Terraform installation
Open a terminal and test:
terraform -v
Generate API keys
Follow the documentation for generating keys on OCI Documentation.
Upload your API keys
Follow the documentation for uploading your keys on OCI Documentation.
Note the fingerprint.
Create an OCI compartment
Follow the documentation for creating a compartment.
Obtain the necessary OCIDs
The following OCIDs are required:
- Compartment OCID
- Tenancy OCID
- User OCID
Follow the documentation for obtaining the tenancy and user ids on OCI Documentation.
To obtain the compartment OCID:
- Navigate to Identity > Compartments
- Click on your Compartment
- Locate OCID on the page and click on 'Copy'
If you wish to encrypt Kubernetes secrets with a key from OCI KMS, you also need to create a vault and a key and obtain the key id.
Configure OCI Policy for OKE
Follow the documentation for to create the necessary OKE policy.
Deploy the OKE Terraform Module
Prerequisites
- Required Keys and OCIDs
- Required IAM policies
git,sshclient to run locally- Terraform
>= 1.2.0to run locally
Provisioning from an OCI Resource Manager Stack
Network
Network resources configured for an OKE cluster.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Cluster
An OKE-managed Kubernetes cluster.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- core_network_security_group
- core_network_security_group_security_rule
- core_instance (operator)
- containerengine_cluster
Node Pool
A standard OKE-managed pool of worker nodes with enhanced feature support.
Configured with mode = "node-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "node-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
You can set the image_type attribute to one of the following values:
oke(default)platformcustom.
When the image_type is equal to oke or platform there is a high risk for the node-pool image to be updated on subsequent terraform apply executions because the module is using a datasource to fetch the latest images available.
To avoid this situation, you can set the image_type to custom and the image_id to the OCID of the image you want to use for the node-pool.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Virtual Node Pool
An OKE-managed Virtual Node Pool.
Configured with mode = "virtual-node-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "virtual-node-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Instance
A set of self-managed Compute Instances for custom user-provisioned worker nodes not managed by an OCI pool, but individually by Terraform.
Configured with mode = "instance" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "instance" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance
Instance Pool
A self-managed Compute Instance Pool for custom user-provisioned worker nodes.
Configured with mode = "instance-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "instance-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance_configuration
- core_instance_pool
Cluster Network
A self-managed HPC Cluster Network.
Configured with mode = "cluster-network" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "cluster-network" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance_configuration
- core_cluster_network
User Guide
- User Guide
Topology
The following resources are created by default:
- 1 VCN with Internet, NAT and Service Gateways
- Route tables for Internet, NAT and Service Gateways
- 1 regional public subnet for the bastion host along with its security list
- 1 regional private subnet for the operator host along with its NSG
- 1 public control plane subnet
- 1 private regional worker subnet
- 1 public regional load balancer
- 1 bastion host
- 1 operator host
- 1 public Kubernetes Cluster with private worker nodes
- 1 Network Security Group (NSG) for each of control plane, workers and load balancers
The Kubernetes Control Plane Nodes run in Oracle's tenancy and are not shown here.
Although the recommended approach is to now deploy private clusters,we are currently keeping the default setting to public. This is to give our users the time to adjust other configurations e.g. their CI/CD tools.
The Load Balancers are only created when Kubernetes services of type LoadBalancer are deployed or you manually create Load Balancers yourself.
The diagrams below depicts the default deployment in multi-AD regions:
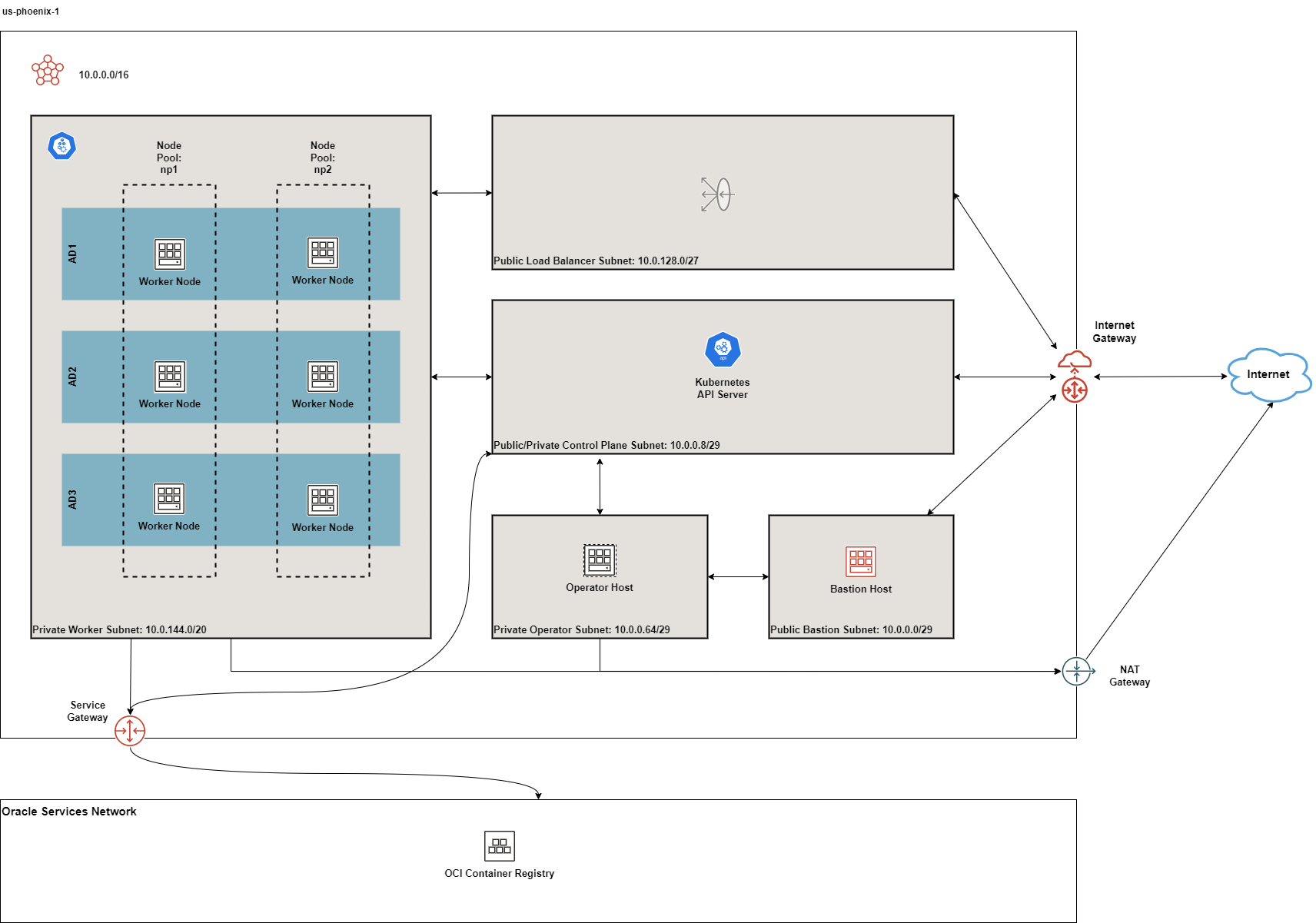 Figure 1: Multi-AD Default Deployment
Figure 1: Multi-AD Default Deployment
and single-AD regions:

The node pools above are depicted for illustration purposes only. By default, the clusters are now created without any node pools.
Networking and Gateways

The following subnets are created by default:
- 1 public regional control plane subnet: this subnet hosts an endpoint for the Kubernetes API server publicly accessible from the Internet. Typically, only 1 IP address is sufficient if you intend to host only 1 OKE cluster in this VCN. However, if you intend to host many OKE or Kubernetes clusters in this VCN and you intend to reuse the same subnets, you need to increase the default size of this subnet.
- 1 private regional worker subnet: this subnet hosts the worker nodes where your workloads will be running. By default, they are private. If you need admin access to the worker nodes e.g. SSH, you'll need to enable and use either the bastion host or the OCI Bastion Service.
- 1 public regional load balancer subnet: this subnet hosts your OCI Load Balancer which acts as a network ingress point into your OKE cluster.
- 1 public regional bastion subnet: this subnet hosts an optional bastion host. See additional documentation on the purpose of the bastion host.
- 1 private regional operator subnet: this subnet hosts an optional operator host that is used for admin purposes. See additional documentation on the purpose of the operator host
The bastion subnet is regional i.e. in multi-AD regions, the subnet spans all Availability Domains. By default, the bastion subnet is assigned a CIDR of 10.0.0.0/29 giving a maximum possible of 5 assignable IP addresses in the bastion subnet.
The workers subnet has a CIDR of 10.0.144.0/20 assigned by default. This gives the subnet a maximum possible of 4093 IP addresses. This is enough to scale the cluster to the maximum number of worker nodes (2000) currently allowed by Oracle Container Engine.
The load balancer subnets are of 2 types:
- public
- private
By default, only the public load balancer subnet is created. See Public and Internal Load Balancers for more details. The private load balancer subnet has a CIDR of 10.0.32.0/27 whereas the public load balancer subnet has a CIDR of 10.0.128.0/27 assigned by default. This allows both subnets to assign a maximum of 29 IP addresses and therefore 9 load balancers can be created in each. You can control the size of your subnets and have more load balancers if required by adjusting the newbit and netnum values for the subnets parameter.
The subnets parameter govern the boundaries and sizes of the subnets. If you need to change the default values, refer to the Networking Documentation to see how. We recommend working with your network administrator to design your network. The following additional documentation is useful in designing your network:
The following gateways are also created:
- Internet Gateway: this is required if the application is public-facing or a public bastion host is used
- NAT Gateway if deployed in private mode
- Service Gateway: this is required for connectivity between worker nodes and the control plane
The Service Gateway also allows OCI cloud resources without public IP addresses to privately access Oracle services and without the traffic going over the public Internet. Refer to the OCI Service Gateway documentation to understand whether you need to enable it.
Bastion Host

The bastion host is created in a public regional subnet. You can create or destroy it anytime with no effect on the Kubernetes cluster by setting the create_bastion_host = true in your variable file. You can also turn it on or off by changing the bastion_state to RUNNING or STOPPED respectively.
By default, the bastion host can be accessed from anywhere. However, you can restrict its access to a defined list of CIDR blocks using the bastion_access parameter. You can also make the bastion host private if you have some alternative connectivity method to your VCN e.g. using VPN.
You can use the bastion host for the following:
- SSH to the worker nodes
- SSH to the operator host to manage your Kubernetes cluster
To SSH to the bastion, copy the command that terraform outputs at the end of its run:
ssh_to_bastion = ssh -i /path/to/private_key opc@bastion_ip
To SSH to the worker nodes, you can do the following:
ssh -i /path/to/private_key -J <username>@bastion_ip opc@worker_node_private_ip
If your private ssh key has a different name or path than the default ~/.ssh/id_* that ssh expects e.g if your private key is ~/.ssh/dev_rsa, you must add it to your ssh agent:
eval $(ssh-agent -s)
ssh-add ~/.ssh/dev_rsa
Public vs Private Clusters
When deployed in public mode, the Kubernetes API endpoint is publicly accessible.

.Accessing the Kubernetes API endpoint publicly image::images/publiccluster.png[align="center"]
You can set the Kubernetes cluster to be public and restrict its access to the CIDR blocks A.B.C.D/A and X.Y.Z.X/Z by using the following parameters:
control_plane_is_public = true # *true/false
control_plane_allowed_cidrs = ["A.B.C.D/A","X.Y.Z.X/Z"]
When deployed in private mode, the Kubernetes endpoint can only be accessed from the operator host or from a defined list of CIDR blocks specified in control_plane_allowed_cidrs. This assumes that you have established some form of connectivity with the VCN via VPN or FastConnect from the networks listed in control_plane_allowed_cidrs.

The following table maps all possible cluster and workers deployment combinations:
| Workers/control plane | public | private |
|---|---|---|
| worker_type=public | X | X |
| worker_type=private | X | X |
Public vs Private worker nodes
Public workers

When deployed in public mode, all worker subnets will be deployed as public subnets and route to the Internet Gateway directly. Worker nodes will have both private and public IP addresses. Their private IP addresses will be from the range of the worker subnet they are part of whereas the public IP addresses will be allocated from Oracle's pool of public IP addresses.
If you intend to use Kubernetes NodePort services on your public workers or SSH to them, you must explicitly enable these in order for the security rules to be properly configured and allow access:
allow_node_port_access = true
allow_worker_ssh_access = true
Because of the increased attack surface area, we do not recommend running your worker nodes publicly. However, there are some valid use cases for these and you have the option to make this choice.
Private workers

When deployed in private mode, the worker subnet will be deployed as a private subnet and route to the NAT Gateway instead. This considerably reduces the surface attack area and improves the security posture of your OKE cluster as well as the rest of your infrastructure.
Irrespective of whether you run your worker nodes publicly or privately, if you ssh to them, you must do so through the bastion host or the OCI Bastion Service. Ensure you have enabled the bastion host.
Public vs. Internal Load Balancers

You can use both public and internal load balancers. By default, OKE creates public load balancers whenever you deploy services of type LoadBalancer. As public load balancers are allocated public IP addresses, they require require a public subnet and the default service load balancer is therefore set to use the public subnet pub-lb.
You can change this default behaviour and use internal load balancers instead. Internal load balancers have only private IP addresses and are not accessible from the Internet. Although you can place internal load balancers in public subnets (they just will not be allocated public IP addresses), we recommend you use a different subnet for internal load balancers.
Depending on your use case, you can also have both public and private load balancers.
Refer to the user guide on load balancers for more details.
Using Public Load Balancers
When creating a service of type LoadBalancer, you must specify the list of NSGs using OCI Load Balancer annotations e.g.:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: acme-website
annotations:
oci.oraclecloud.com/oci-network-security-groups: "ocid1.networksecuritygroup...."
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-security-list-management-mode: "None"
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
....
Since we have already added the NodePort range to the public load balancer NSG, you can also disable the security list management and set its value to "None".
Using Internal Load Balancers
When creating an internal load balancer, you must ensure the following:
load_balancersis set tobothorinternal.
Setting the load_balancers parameter to both or internal only ensures the private subnet for internal load balancers and the required NSG is created. To set it as the default subnet for your service load balancer, set the preferred_load_balancer to internal. In this way, if you happen to use both types of Load Balancers, the cluster will preference the internal load balancer subnets instead.
Even if you set the preferred_load_balancer to internal, you still need to set the correct service annotation when creating internal load balancers. Just setting the subnet to be private is not sufficient e.g.
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-internal: "true"
Refer to OCI Documentation for further guidance on internal load balancers.
Creating LoadBalancers using IngressControllers
You may want to refer to the following articles exploring Ingress Controllers and Load Balancers for additional information:
- Experimenting with Ingress Controllers on Oracle Container Engine (OKE) Part 1
- [Experimenting with Ingress Controllers on Oracle Container Engine (OKE) Part 1]
Identity
Optional creation of Identity Dynamic Groups, Policies, and Tags.
Identity: Policies
Usage
create_iam_autoscaler_policy = "auto" // never/*auto/always
create_iam_kms_policy = "auto" // never/*auto/always
create_iam_operator_policy = "auto" // never/*auto/always
create_iam_worker_policy = "auto" // never/*auto/always
References
- Managing Dynamic Groups
- Managing Policies
- Policy Configuration for Cluster Creation and Deployment
- About Access Control and OCI Kubernetes Engine
- KMS
Identity: Tags
Usage
create_iam_tag_namespace = false // true/*false
create_iam_defined_tags = false // true/*false
tag_namespace = "oke"
use_defined_tags = false // true/*false
References
Network
Optional creation of VCN subnets, Network Security Groups, NSG Rules, and more.
Examples
Create Minimal Network Resources
TODO: ../../../examples/network/vars-network-only-minimal.auto.tfvars
# All configuration for network sub-module w/ defaults
# Virtual Cloud Network (VCN)
assign_dns = true # *true/false
create_vcn = true # *true/false
local_peering_gateways = {}
lockdown_default_seclist = true # *true/false
vcn_id = null # Ignored if create_vcn = true
vcn_cidrs = ["10.0.0.0/16"] # Ignored if create_vcn = false
vcn_dns_label = "oke" # Ignored if create_vcn = false
vcn_name = "oke" # Ignored if create_vcn = false
enable_ipv6 = false # true/*false
Create Common Network Resources
# All configuration for network sub-module w/ defaults
# Virtual Cloud Network (VCN)
assign_dns = true # *true/false
create_vcn = true # *true/false
local_peering_gateways = {}
lockdown_default_seclist = true # *true/false
vcn_id = null # Ignored if create_vcn = true
vcn_cidrs = ["10.0.0.0/16"] # Ignored if create_vcn = false
vcn_dns_label = "oke" # Ignored if create_vcn = false
vcn_name = "oke" # Ignored if create_vcn = false
enable_ipv6 = false # true/*false
# Subnets
subnets = {
bastion = { newbits = 13 }
operator = { newbits = 13 }
cp = { newbits = 13 }
int_lb = { newbits = 11 }
pub_lb = { newbits = 11 }
workers = { newbits = 2 }
pods = { newbits = 2 }
}
# Security
allow_node_port_access = true # *true/false
allow_pod_internet_access = true # *true/false
allow_worker_internet_access = false # true/*false
allow_worker_ssh_access = false # true/*false
control_plane_allowed_cidrs = ["0.0.0.0/0"] # e.g. "0.0.0.0/0"
control_plane_nsg_ids = [] # Additional NSGs combined with created
control_plane_type = "public" # public/*private
enable_waf = false # true/*false
load_balancers = "both" # public/private/*both
preferred_load_balancer = "public" # public/*private
worker_nsg_ids = [] # Additional NSGs combined with created
worker_type = "private" # public/*private
# See https://www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers/protocol-numbers.xhtml
# Protocols: All = "all"; ICMP = 1; TCP = 6; UDP = 17
# Source/destination type: NSG ID: "NETWORK_SECURITY_GROUP"; CIDR range: "CIDR_BLOCK"
allow_rules_internal_lb = {
# "Allow TCP ingress to internal load balancers for port 8080 from VCN" : {
# protocol = 6, port = 8080, source = "10.0.0.0/16", source_type = "CIDR_BLOCK",
# },
}
allow_rules_public_lb = {
# "Allow TCP ingress to public load balancers for SSL traffic from anywhere" : {
# protocol = 6, port = 443, source = "0.0.0.0/0", source_type = "CIDR_BLOCK",
# },
# "Allow UDP egress to workers port range 50000-52767 from Public LBs" : {
# protocol = 17, destination_port_min = 50000, destination_port_max=52767, destination = "workers", destination_type = "NETWORK_SECURITY_GROUP"
# },
}
allow_rules_workers = {
# "Allow TCP ingress to workers for port 8080 from VCN" : {
# protocol = 6, port = 8080, source = "10.0.0.0/16", source_type = "CIDR_BLOCK",
# },
# "Allow UDP ingress to workers for port range 50000-52767 from Public LBs" : {
# protocol = 17, destination_port_min = 50000, destination_port_max=52767, source = "pub_lb", source_type = "NETWORK_SECURITY_GROUP"
# },
# "Allow TCP ingress to workers for port range 8888-8888 from existing NSG" : {
# protocol = 6, destination_port_min = 8888, destination_port_max=8888, source = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup.oc1.eu-frankfurt-1.aaaaaaaai6z4le2ji7dkpmuwff4525b734wrjlifjqkrzlr5qctgxdsyoyra", source_type = "NETWORK_SECURITY_GROUP"
# },
}
# Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
create_drg = false # true/*false
drg_display_name = "drg"
drg_id = null
# Routing
ig_route_table_id = null # Optional ID of existing internet gateway route table
internet_gateway_id = null # Optional ID of existing internet gateway
internet_gateway_route_rules = [
# {
# destination = "192.168.0.0/16" # Route Rule Destination CIDR
# destination_type = "CIDR_BLOCK" # only CIDR_BLOCK is supported at the moment
# network_entity_id = "drg" # for internet_gateway_route_rules input variable, you can use special strings "drg", "internet_gateway" or pass a valid OCID using string or any Named Values
# description = "Terraformed - User added Routing Rule: To drg provided to this module. drg_id, if available, is automatically retrieved with keyword drg"
# },
]
igw_ngw_mixed_route_id = null # Optional ID of existing mixed route table NAT GW for IPv4 and Internet GW for IPv6
nat_gateway_id = null # Optional ID of existing NAT gateway
nat_gateway_public_ip_id = "none"
nat_route_table_id = null # Optional ID of existing NAT gateway route table
nat_gateway_route_rules = [
# {
# destination = "192.168.0.0/16" # Route Rule Destination CIDR
# destination_type = "CIDR_BLOCK" # only CIDR_BLOCK is supported at the moment
# network_entity_id = "drg" # for nat_gateway_route_rules input variable, you can use special strings "drg", "nat_gateway" or pass a valid OCID using string or any Named Values
# description = "Terraformed - User added Routing Rule: To drg provided to this module. drg_id, if available, is automatically retrieved with keyword drg"
# },
]
# Experimental
use_stateless_rules = true # Use stateless rules for security lists and network security groups instead of the default stateful rules.
# Note that the egress rule to 0.0.0.0/0 from pods and workers will be statefull independent of this setting because of security concerns.
References
Subnets
Subnets are created for core components managed within the module, namely:
- Bastion
- Operator
- Control plane (
cp) - Workers
- Pods
- Internal load balancers (
int_lb) - Public load balancers (
pub_lb)
Create new subnets (automatic)
subnets = {
bastion = { newbits = 13 }
operator = { newbits = 13 }
cp = { newbits = 13 }
int_lb = { newbits = 11 }
pub_lb = { newbits = 11 }
workers = { newbits = 2 }
pods = { newbits = 2 }
}
Create new subnets (forced)
subnets = {
bastion = {
create = "always",
netnum = 0,
newbits = 13
}
operator = {
create = "always",
netnum = 1,
newbits = 13
}
cp = {
create = "always",
netnum = 2,
newbits = 13
}
int_lb = {
create = "always",
netnum = 16,
newbits = 11
}
pub_lb = {
create = "always",
netnum = 17,
newbits = 11
}
workers = {
create = "always",
netnum = 1,
newbits = 2
}
}
Create new subnets (CIDR notation)
subnets = {
bastion = { cidr = "10.0.0.0/29" }
operator = { cidr = "10.0.0.64/29" }
cp = { cidr = "10.0.0.8/29" }
int_lb = { cidr = "10.0.0.32/27" }
pub_lb = { cidr = "10.0.128.0/27" }
workers = { cidr = "10.0.144.0/20" }
pods = { cidr = "10.0.64.0/18" }
}
Create new subnets with IPv4 and IPv6 (CIDR notation)
subnets = {
bastion = { cidr = "10.0.0.0/29", ipv6_cidr = "8, 0" }
operator = { cidr = "10.0.0.64/29", ipv6_cidr = "8, 1" }
cp = { cidr = "10.0.0.8/29", ipv6_cidr = "8, 2" }
int_lb = { cidr = "10.0.0.32/27", ipv6_cidr = "8, 3" }
pub_lb = { cidr = "10.0.128.0/27", ipv6_cidr = "8, 4" }
workers = { cidr = "10.0.144.0/20", ipv6_cidr = "2603:c020:8010:f002::/64" }
pods = { cidr = "10.0.64.0/18", ipv6_cidr = "2603:c020:8010:f003::/64" }
}
Use existing subnets
subnets = {
operator = { id = "ocid1.subnet..." }
cp = { id = "ocid1.subnet..." }
int_lb = { id = "ocid1.subnet..." }
pub_lb = { id = "ocid1.subnet..." }
workers = { id = "ocid1.subnet..." }
pods = { id = "ocid1.subnet..." }
}
References
- OCI Networking Overview
- VCNs and Subnets
- Terraform cidrsubnets function
Network Security Groups
Network Security Groups (NSGs) are used to permit network access between resources creation by the module, namely:
- Bastion
- Operator
- Control plane (
cp) - Workers
- Pods
- Internal load balancers (
int_lb) - Public load balancers (
pub_lb)
Create new NSGs
nsgs = {
bastion = {}
operator = {}
cp = {}
int_lb = {}
pub_lb = {}
workers = {}
pods = {}
}
Use existing NSGs
nsgs = {
bastion = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
operator = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
cp = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
int_lb = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
pub_lb = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
workers = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
pods = { id = "ocid1.networksecuritygroup..." }
}
References
Cluster
See also:
The OKE parameters concern mainly the following:
- whether you want your OKE control plane to be public or private
- whether to assign a public IP address to the API endpoint for public access
- whether you want to deploy public or private worker nodes
- whether you want to allow NodePort or ssh access to the worker nodes
- Kubernetes options such as dashboard, networking
- number of node pools and their respective size of the cluster
- services and pods cidr blocks
- whether to use encryption
- whether you want to enable dual-stack: IPv4 & IPv6
If you need to change the default services and pods' CIDRs, note the following:
- The CIDR block you specify for the VCN must not overlap with the CIDR block you specify for the Kubernetes services.
- The CIDR blocks you specify for pods running in the cluster must not overlap with CIDR blocks you specify for worker node and load balancer subnets.
Example usage
Basic cluster with defaults:
cluster_name = "oke-example"
kubernetes_version = "v1.34.1"
Enhanced cluster with extra configuration:
create_cluster = true // *true/false
cluster_dns = null
cluster_kms_key_id = null
cluster_name = "oke"
cluster_type = "enhanced" // *basic/enhanced
cni_type = "flannel" // *flannel/npn
assign_public_ip_to_control_plane = true // true/*false
image_signing_keys = []
kubernetes_version = "v1.34.1"
pods_cidr = "10.244.0.0/16"
services_cidr = "10.96.0.0/16"
use_signed_images = false // true/*false
enable_ipv6 = false //true/*false
backend_nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."] // the workers and pods NSGs are always added.
OpenID Connect Authentication
By default, OKE clusters are set up to authenticate individuals (human users, groups or service principals) accessing the API endpoint using OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Using OKE OIDC Authentication, we can authenticate OKE API Endpoint requests (from human users or service principals) using tokens issued by third-party Identity Providers without the need for federation with OCI IAM.
Prerequisites
Note the following prerequisites for enabling a cluster for OIDC authentication:
- The cluster must be an enhanced cluster. OIDC authentication is not supported for basic clusters.
- The cluster must be running Kubernetes version 1.21 (or later) -- for single external OIDC IdP setup.
- The cluster must be running Kubernetes version 1.30 (or later) -- for multiple external OIDC IdPs setup.
Configuration
In addition to the implicit OCI IAM, you can configure the OKE cluster to authenticate the cluster API endpoint requests using a single external OIDC (OpenID Connect) Identity Provider (IdP).
For this is necessary to set the following variables:
oidc_discovery_enabled = true
oidc_token_authentication_config = {
client_id = ...,
issuer_url = ...,
username_claim = ...,
username_prefix = ...,
groups_claim = ...,
groups_prefix = ...,
required_claims = [
{
key = ...,
value = ...
},
{
key = ...,
value = ...
}
],
ca_certificate = ...,
signing_algorithms = []
}
In case you're looking to authenticate the cluster API endpoint requests with multiple OIDC IdPs, you can take advantage of the authentication configuration via file Kubernetes feature.
oidc_discovery_enabled = true
oidc_token_authentication_config = {
configuration_file = base64encode(yamlencode(
{
"apiVersion" = "apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1beta1"
"kind" = "AuthenticationConfiguration"
"jwt" = [
{
"issuer"= {
"url" = "...",
"audiences" = [
"..."
],
"audienceMatchPolicy" = "MatchAny"
}
"claimMappings" = {
"username" = {
"claim" = "..."
"prefix" = ""
}
}
"claimValidationRules" = [
{
"claim" = "..."
"requiredValue" = "..."
}
]
}
]
}
))
}
The authenticated users are mapped to a User resource in Kubernetes and you have to setup the desired RBAC polices to provide access.
E.g. for Github Action workflow:
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: actions-oidc-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list", "create", "update", "delete"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: actions-oidc-binding
namespace: default
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: actions-oidc-role
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: User
name: actions-oidc:repo:GH-ACCOUNT/GH-REPO:ref:refs/heads/main
Note:
- You need to make sure the OKE Control Plane endpoint is allowed to connect to the IdP.
allow_rules_cp = {
"Allow egress to anywhere HTTPS from OKE CP" : {
protocol = "6", port=443, destination = "0.0.0.0/0", destination_type = "CIDR_BLOCK",
}
}
- You cannot configure cluster OIDC Authentication using the arguments of the
oidc_token_authentication_config(client_id,issuer_url, etc..) and theconfiguration_fileat the same time.
OpenID Connect Discovery
Prerequisites
Note the following points when using OIDC Discovery:
- The cluster must be an enhanced cluster. OIDC Discovery is not supported for basic clusters.
- The cluster must be running Kubernetes version 1.21 (or later).
Configuration
OKE already supports Workload Identity to enable Kubernetes pods to access OCI resources, such as a secret or cloud storage bucket without storing access credentials in your Kubernetes cluster.
If you are looking to authorize Kubernetes pods to access non-OCI resources you can enable OKE OIDC Discovery.
When you enable OIDC discovery for an OKE cluster, OKE provides an OpenID Connect issuer endpoint. This endpoint serves the OIDC discovery document and the JSON web key set (JWKS), which contain the public key necessary for token validation. These resources enable third-party IdP to validate tokens issued for pods in the OKE cluster, allowing those pods to access non-OCI resources.
To enable the OKE OIDC Discovery, you have to set the following variable:
open_id_connect_discovery_enabled = true
The OpenID Connect issuer endpoint is available in the output:
cluster_oidc_discovery_endpoint
Example usage
OIDC Authentication setup using Kubernetes API server flags
{{#include ../../../examples/cluster-addons/vars-cluster-oidc-auth-single.auto.tfvars:4:}}
OIDC Authentication setup using Kubernetes API server configuration file
{{#include ../../../examples/cluster-addons/vars-cluster-oidc-auth-multiple.auto.tfvars:4:}}
Reference
- OKE OpenID Authetication
- OKE Cluster Terraform resource
- Github workflow OKE OIDC authentication
- Kubernetes OIDC Authentication setup using Kubernetes API server configuration file
- Kubernetes OIDC Authentication setup using Kubernetes API server flags
OpenID Connect Discovery
With OKE OIDC Discovery, it is possible to validate Kubernetes pods running on OKE clusters with third-party STS (Security Token Service) issuers, whether on-premises or in cloud service providers (CSPs) such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and authorize them to access non-OCI resources. OKE OIDC Discovery enables this integration.
Prerequisites
Note the following points when using OIDC Discovery:
- The cluster must be an enhanced cluster. OIDC Discovery is not supported for basic clusters.
- The cluster must be running Kubernetes version 1.21 (or later).
Configuration
When you enable OIDC discovery for an OKE cluster, OKE provides an OpenID Connect issuer endpoint. This endpoint serves the OIDC discovery document and the JSON web key set (JWKS), which contain the public key necessary for token validation. These resources enable third-party IdP to validate tokens issued for pods in the OKE cluster, allowing those pods to access non-OCI resources.
To enable the OKE OIDC Discovery, you have to set the following variable:
open_id_connect_discovery_enabled = true
The OpenID Connect issuer endpoint is available in the output:
cluster_oidc_discovery_endpoint
Example usage
OIDC Discovery setup using Kubernetes API server flags
{{#include ../../../examples/cluster-addons/vars-cluster-oidc-discovery.auto.tfvars:4:}}
Reference
Cluster Add-ons
With this module you can manage both essential and optional add-ons on enhanced OKE clusters.
This module provides the option to remove Essential addons and to manage, both essential & optional addons.
Cluster add-on removal (using the cluster_addons_to_remove variable) requires the creation of the operator host.
To list the available cluster add-ons for a specific Kubernetes version you can run the following oci-cli command:
oci ce addon-option list --kubernetes-version <k8s-version>
Note: For the cluster autoscaler you should choose only one of the options:
- the stand-alone cluster-autoscaler deployment, using the extension module
- the cluster-autoscaler add-on
When customizing the configuration of an existing addon, use the flag override_existing=true. Default value is false if not specified.
Example usage
cluster_addons = {
"CertManager" = {
remove_addon_resources_on_delete = true
override_existing = true # Default is false if not specified
# The list of supported configurations for the cluster addons is here: https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/ContEng/Tasks/contengconfiguringclusteraddons-configurationarguments.htm#contengconfiguringclusteraddons-configurationarguments_CertificateManager
configurations = [
{
key = "numOfReplicas"
value = "1"
}
]
}
# The NvidiaGpuPlugin is disabled by default. To enable it, add the following block to the cluster_addons variable
"NvidiaGpuPlugin" = {
remove_addon_resources_on_delete = true
},
# Prevent Flannel pods from being scheduled using a non-existing label as nodeSelector
"Flannel" = {
remove_addon_resources_on_delete = true
override_existing = true # Override the existing configuration with this one, if Flannel addon in already enabled
configurations = [
{
key = "nodeSelectors"
value = "{\"addon\":\"no-schedule\"}"
}
],
},
# Prevent Kube-Proxy pods from being scheduled using a non-existing label as nodeSelector
"KubeProxy" = {
remove_addon_resources_on_delete = true
override_existing = true # Override the existing configuration with this one, if KubeProxy addon in already enabled
configurations = [
{
key = "nodeSelectors"
value = "{\"addon\":\"no-schedule\"}"
}
],
}
}
cluster_addons_to_remove = {
Flannel = {
remove_k8s_resources = true
}
}
Reference
Workers
The worker_pools input defines worker node configuration for the cluster.
Many of the global configuration values below may be overridden on each pool definition or omitted for defaults, with the worker_ or worker_pool_ variable prefix removed, e.g. worker_image_id overridden with image_id.
For example:
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
worker_pool_size = 1
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-standard = {},
oke-vm-standard-large = {
description = "OKE-managed Node Pool with OKE Oracle Linux 8 image",
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
create = true,
ocpus = 8,
memory = 128,
boot_volume_size = 200,
os = "Oracle Linux",
os_version = "8",
},
}
Workers: Mode
The mode parameter controls the type of resources provisioned in OCI for OKE worker nodes.
Workers / Mode: Node Pool
A standard OKE-managed pool of worker nodes with enhanced feature support.
Configured with mode = "node-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "node-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
You can set the image_type attribute to one of the following values:
oke(default)platformcustom.
When the image_type is equal to oke or platform there is a high risk for the node-pool image to be updated on subsequent terraform apply executions because the module is using a datasource to fetch the latest images available.
To avoid this situation, you can set the image_type to custom and the image_id to the OCID of the image you want to use for the node-pool.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Usage
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
worker_pool_size = 1
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-standard = {},
oke-vm-standard-large = {
size = 1,
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 8,
memory = 128,
boot_volume_size = 200,
create = false,
},
oke-vm-standard-ol7 = {
description = "OKE-managed Node Pool with OKE Oracle Linux 7 image",
size = 1,
os = "Oracle Linux",
os_version = "7",
create = false,
},
oke-vm-standard-ol8 = {
description = "OKE-managed Node Pool with OKE Oracle Linux 8 image",
size = 1,
os = "Oracle Linux",
os_version = "8",
},
oke-vm-standard-custom = {
description = "OKE-managed Node Pool with custom image",
image_type = "custom",
image_id = "ocid1.image...",
size = 1,
create = false,
},
}
References
- oci_containerengine_node_pool
- Modifying Node Pool and Worker Node Properties
- Adding and Removing Node Pools
Workers / Mode: Virtual Node Pool
An OKE-managed Virtual Node Pool.
Configured with mode = "virtual-node-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "virtual-node-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Usage
worker_pools = {
oke-virtual = {
description = "OKE-managed Virtual Node Pool",
mode = "virtual-node-pool",
size = 1,
},
}
References
Workers / Mode: Instance
A set of self-managed Compute Instances for custom user-provisioned worker nodes not managed by an OCI pool, but individually by Terraform.
Configured with mode = "instance" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "instance" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance
Usage
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-instance = {
description = "Self-managed Instances",
mode = "instance",
size = 1,
node_labels = {
"keya" = "valuea",
"keyb" = "valueb"
},
secondary_vnics = {
"vnic-display-name" = {},
},
},
oke-vm-instance-burst = {
description = "Self-managed Instance With Bursting",
mode = "instance",
size = 1,
burst = "BASELINE_1_8", # Valid values BASELINE_1_8,BASELINE_1_2
},
}
Instance agent configuration:
worker_pools = {
oke-instance = {
agent_config = {
are_all_plugins_disabled = false,
is_management_disabled = false,
is_monitoring_disabled = false,
plugins_config = {
"Bastion" = "DISABLED",
"Block Volume Management" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Authentication" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Auto-Configuration" = "DISABLED",
"Compute Instance Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Compute Instance Run Command" = "ENABLED",
"Compute RDMA GPU Monitoring" = "DISABLED",
"Custom Logs Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Management Agent" = "ENABLED",
"Oracle Autonomous Linux" = "DISABLED",
"OS Management Service Agent" = "DISABLED",
}
}
},
}
References
Workers / Mode: Instance Pool
A self-managed Compute Instance Pool for custom user-provisioned worker nodes.
Configured with mode = "instance-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "instance-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance_configuration
- core_instance_pool
Usage
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-instance-pool = {
description = "Self-managed Instance Pool with custom image",
mode = "instance-pool",
size = 1,
node_labels = {
"keya" = "valuea",
"keyb" = "valueb"
},
secondary_vnics = {
"vnic-display-name" = {},
},
},
oke-vm-instance-pool-burst = {
description = "Self-managed Instance Pool With Bursting",
mode = "instance-pool",
size = 1,
burst = "BASELINE_1_8", # Valid values BASELINE_1_8,BASELINE_1_2
},
oke-vm-instance-pool-with-block-volume = {
description = "Self-managed Instance Pool with block volume",
mode = "instance-pool",
size = 1,
disable_block_volume = false,
block_volume_size_in_gbs = 60,
},
oke-vm-instance-pool-without-block-volume = {
description = "Self-managed Instance Pool without block volume",
mode = "instance-pool",
size = 1,
disable_block_volume = true,
},
}
Instance agent configuration:
worker_pools = {
oke-instance = {
agent_config = {
are_all_plugins_disabled = false,
is_management_disabled = false,
is_monitoring_disabled = false,
plugins_config = {
"Bastion" = "DISABLED",
"Block Volume Management" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Authentication" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Auto-Configuration" = "DISABLED",
"Compute Instance Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Compute Instance Run Command" = "ENABLED",
"Compute RDMA GPU Monitoring" = "DISABLED",
"Custom Logs Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Management Agent" = "ENABLED",
"Oracle Autonomous Linux" = "DISABLED",
"OS Management Service Agent" = "DISABLED",
}
}
},
}
References
Workers / Mode: Cluster Network
A self-managed HPC Cluster Network.
Configured with mode = "cluster-network" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "cluster-network" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance_configuration
- core_cluster_network
Usage
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-standard = {
description = "Managed node pool for operational workloads without GPU toleration"
mode = "node-pool",
size = 1,
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 2,
memory = 16,
boot_volume_size = 50,
},
oke-bm-gpu-rdma = {
description = "Self-managed nodes in a Cluster Network with RDMA networking",
mode = "cluster-network",
size = 1,
shape = "BM.GPU.B4.8",
placement_ads = [1],
image_id = "ocid1.image..."
cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo "Pool-specific cloud_init using shell script"
EOT
},
],
secondary_vnics = {
"vnic-display-name" = {
nic_index = 1,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
},
}
}
Instance agent configuration:
worker_pools = {
oke-instance = {
agent_config = {
are_all_plugins_disabled = false,
is_management_disabled = false,
is_monitoring_disabled = false,
plugins_config = {
"Bastion" = "DISABLED",
"Block Volume Management" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Authentication" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Auto-Configuration" = "DISABLED",
"Compute Instance Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Compute Instance Run Command" = "ENABLED",
"Compute RDMA GPU Monitoring" = "DISABLED",
"Custom Logs Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Management Agent" = "ENABLED",
"Oracle Autonomous Linux" = "DISABLED",
"OS Management Service Agent" = "DISABLED",
}
}
},
}
References
- Cluster Networks with Instance Pools
- Large Clusters, Lowest Latency: Cluster Networking on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- First principles: Building a high-performance network in the public cloud
- Running Applications on Oracle Cloud Using Cluster Networking
Workers / Mode: Compute Clusters
Create self-managed HPC Compute Clusters.
A compute cluster is a group of high performance computing (HPC), GPU, or optimized instances that are connected with a high-bandwidth, ultra low-latency network.
- BM.GPU.A100-v2.8
- BM.GPU.H100.8
- BM.GPU4.8
- BM.HPC2.36
- BM.Optimized3.36
Configured with mode = "compute-cluster" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "compute-cluster" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
Compute clusters shared by multiple worker groups must be created using the variable worker_compute_clusters and should be referenced by the key in the compute_cluster attribute of the worker group.
If the worker_compute_clusters is not specified, the module will create a compute cluster per each worker group.
Usage
worker_compute_clusters = { # Use this variable to define a compute cluster you intend to use with multiple-nodepools.
"shared" = {
placement_ad = 1
}
}
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-standard = {
description = "Managed node pool for operational workloads without GPU toleration"
mode = "node-pool",
size = 1,
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 2,
memory = 16,
boot_volume_size = 50,
},
compute-cluster-group-1 = {
shape = "BM.HPC2.36",
boot_volume_size = 100,
image_id = "ocid1.image.oc1..."
image_type = "custom"
mode = "compute-cluster"
compute_cluster = "shared"
instance_ids = ["1", "2", "3"] # List of instance IDs in the compute cluster. Each instance ID corresponds to a separate node in the cluster.
placement_ad = "1"
cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo "Pool-specific cloud_init using shell script"
EOT
},
],
secondary_vnics = {
"vnic-display-name" = {
nic_index = 1,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
},
}
compute-cluster-group-2 = {
shape = "BM.HPC2.36",
boot_volume_size = 100,
image_id = "ocid1.image.oc1..."
image_type = "custom"
mode = "compute-cluster"
compute_cluster = "shared"
instance_ids = ["a", "b", "c"] # List of instance IDs in the compute cluster. Each instance ID corresponds to a separate node in the cluster.
placement_ad = "1"
cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo "Pool-specific cloud_init using shell script"
EOT
},
],
secondary_vnics = {
"vnic-display-name" = {
nic_index = 1,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
},
}
compute-cluster-group-3 = {
shape = "BM.HPC2.36",
boot_volume_size = 100,
image_id = "ocid1.image.oc1..."
image_type = "custom"
mode = "compute-cluster"
instance_ids = ["001", "002", "003"] # List of instance IDs in the compute cluster. Each instance ID corresponds to a separate node in the cluster.
placement_ad = "1"
cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo "Pool-specific cloud_init using shell script"
EOT
},
],
}
}
Instance agent configuration:
worker_pools = {
oke-instance = {
agent_config = {
are_all_plugins_disabled = false,
is_management_disabled = false,
is_monitoring_disabled = false,
plugins_config = {
"Bastion" = "DISABLED",
"Block Volume Management" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Authentication" = "DISABLED",
"Compute HPC RDMA Auto-Configuration" = "DISABLED",
"Compute Instance Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Compute Instance Run Command" = "ENABLED",
"Compute RDMA GPU Monitoring" = "DISABLED",
"Custom Logs Monitoring" = "ENABLED",
"Management Agent" = "ENABLED",
"Oracle Autonomous Linux" = "DISABLED",
"OS Management Service Agent" = "DISABLED",
}
}
},
}
References
- Compute Clusters
- Large Clusters, Lowest Latency: Cluster Networking on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- First principles: Building a high-performance network in the public cloud
- Running Applications on Oracle Cloud Using Cluster Networking
Workers: Network
Subnets
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
worker_pool_size = 1
worker_subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-custom-subnet-flannel = {
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
oke-vm-custom-subnet-npn = {
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
pod_subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..." // when cni_type = "npn"
},
}
Network Security Groups
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
worker_pool_size = 1
worker_nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
pod_nsg_ids = [] // when cni_type = "npn"
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-custom-nsgs-flannel = {
nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
},
oke-vm-custom-nsgs-npn = {
nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
pod_nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."] // when cni_type = "npn"
},
}
Secondary VNICs
On pools with a self-managed mode:
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
worker_pool_size = 1
kubeproxy_mode = "iptables" // *iptables/ipvs
worker_is_public = false
assign_public_ip = false
worker_nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
worker_subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
max_pods_per_node = 110
pod_nsg_ids = [] // when cni_type = "npn"
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-custom-network-flannel = {
assign_public_ip = false,
create = false,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
},
oke-vm-custom-network-npn = {
assign_public_ip = false,
create = false,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
pod_subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
pod_nsg_ids = ["ocid1.networksecuritygroup..."]
},
oke-vm-vnics = {
mode = "instance-pool",
size = 1,
create = false,
secondary_vnics = {
vnic0 = {
nic_index = 0,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
vnic1 = {
nic_index = 1,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
},
},
oke-bm-vnics = {
mode = "cluster-network",
size = 2,
shape = "BM.GPU.B4.8",
placement_ads = [1],
create = false,
secondary_vnics = {
gpu0 = {
nic_index = 0,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
gpu1 = {
nic_index = 1,
subnet_id = "ocid1.subnet..."
},
},
},
}
Workers: Image
The operating system image for worker nodes may be defined both globally and on each worker pool.
Recommended base images:
Workers: Cloud-Init
Custom actions may be configured on instance startup in an number of ways depending on the use-case and preferences.
See also:
Global
Cloud init configuration applied to all workers:
worker_cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
runcmd:
- echo "Global cloud_init using cloud-config"
EOT
content_type = "text/cloud-config",
},
{
content = "/path/to/file"
content_type = "text/cloud-boothook",
},
{
content = "<Base64-encoded content>"
content_type = "text/x-shellscript",
},
]
Pool-specific
Cloud init configuration applied to a specific worker pool:
worker_pools = {
pool_default = {}
pool_custom = {
cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
runcmd:
- echo "Pool-specific cloud_init using cloud-config"
EOT
content_type = "text/cloud-config",
},
{
content = "/path/to/file"
content_type = "text/cloud-boothook",
},
{
content = "<Base64-encoded content>"
content_type = "text/x-shellscript",
},
]
}
}
Default Cloud-Init Disabled
When providing a custom script that calls OKE initialization:
worker_disable_default_cloud_init = true
Workers: Scaling
There are two easy ways to add worker nodes to a cluster:
- Add entries to
worker_pools. - Increase the
sizeof aworker_poolsentry.
Worker pools can be added and removed, their size and boot volume size can be updated. After each change, run terraform apply.
Scaling changes to the number and size of pools are immediate after changing the parameters and running terraform apply. The changes to boot volume size will only be effective in newly created nodes after the change is completed.
Autoscaling
See Extensions/Cluster Autoscaler.
Examples
Workers: Storage
TODO
Workers: Draining
Usage
worker_pool_mode = "node-pool"
worker_pool_size = 1
# Configuration for draining nodes through operator
worker_drain_ignore_daemonsets = true
worker_drain_delete_local_data = true
worker_drain_timeout_seconds = 900
worker_pools = {
oke-vm-active = {
description = "Node pool with active workers",
size = 2,
},
oke-vm-draining = {
description = "Node pool with scheduling disabled and draining through operator",
drain = true,
},
oke-vm-disabled = {
description = "Node pool with resource creation disabled (destroyed)",
create = false,
},
oke-managed-drain = {
description = "Node pool with custom settings for managed cordon & drain",
eviction_grace_duration = 30, # specified in seconds
is_force_delete_after_grace_duration = true
},
}
Example
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# module.workers_only.module.utilities[0].null_resource.drain_workers[0] will be created
+ resource "null_resource" "drain_workers" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ triggers = {
+ "drain_commands" = jsonencode(
[
+ "kubectl drain --timeout=900s --ignore-daemonsets=true --delete-emptydir-data=true -l oke.oraclecloud.com/pool.name=oke-vm-draining",
]
)
+ "drain_pools" = jsonencode(
[
+ "oke-vm-draining",
]
)
}
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
module.workers_only.module.utilities[0].null_resource.drain_workers[0] (remote-exec): node/10.200.220.157 cordoned
module.workers_only.module.utilities[0].null_resource.drain_workers[0] (remote-exec): WARNING: ignoring DaemonSet-managed Pods: kube-system/csi-oci-node-99x74, kube-system/kube-flannel-ds-spvsp, kube-system/kube-proxy-6m2kk, ...
module.workers_only.module.utilities[0].null_resource.drain_workers[0] (remote-exec): node/10.200.220.157 drained
module.workers_only.module.utilities[0].null_resource.drain_workers[0]: Creation complete after 18s [id=7686343707387113624]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Observe that the node(s) are now disabled for scheduling, and free of workloads other than DaemonSet-managed Pods when worker_drain_ignore_daemonsets = true (default):
kubectl get nodes -l oke.oraclecloud.com/pool.name=oke-vm-draining
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
10.200.220.157 Ready,SchedulingDisabled node 24m v1.26.2
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces --field-selector spec.nodeName=10.200.220.157
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system csi-oci-node-99x74 1/1 Running 0 50m
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-spvsp 1/1 Running 0 50m
kube-system kube-proxy-6m2kk 1/1 Running 0 50m
kube-system proxymux-client-2r6lk 1/1 Running 0 50m
Run the following command to uncordon a previously drained worker pool. The drain = true setting should be removed from the worker_pools entry to avoid re-draining the pool when running Terraform in the future.
kubectl uncordon -l oke.oraclecloud.com/pool.name=oke-vm-draining
node/10.200.220.157 uncordoned
References
Workers: Node Cycle
Cycling nodes simplifies both the upgrading of the Kubernetes and host OS versions running on the managed worker nodes, and the updating of other worker node properties.
When you set node_cycling_enabled to true for a node pool, OKE will compare the properties of the existing nodes in the node pool with the properties of the node_pool. If any of the following attributes is not aligned, the node is marked for replacement:
kubernetes_versionnode_labelscompute_shape(shape,ocpus,memory)boot_volume_sizeimage_idnode_metadatassh_public_keycloud_initnsg_idsvolume_kms_key_idpv_transit_encryption
The node_cycling_max_surge (default: 1) and node_cycling_max_unavailable (default: 0) node_pool attributes can be configured with absolute values or percentage values, calculated relative to the node_pool size. These attributes determine how OKE will replace the nodes with a stale config in the node_pool.
The node_cycling_mode attribute supports two node cycling modes:
instance- (default) - cycling deletes and recreates a new node with the changes applied.boot_volumecycling swaps the boot volume on the same node.
Notes:
- Only a subset of fields (
kubernetes_version,image_id,boot_volume_size,node_metadata,ssh_public_key,volume_kms_key_id) can be changed withboot_volumecycling. - The cycling operation will attempt to bring all nodes in the NodePool in sync with the NodePool specification. If
boot_volumecycling mode is chosen, and the node needs changes to fields that can not be updated via aboot_volumecycle, the cycle attempt for that node will fail. The cycle_mode has to be changed toinstanceand the node-cycle operation needs to be retried.
When cycling nodes, the OKE cordons, drains, and terminates nodes according to the node pool's cordon and drain options.
Notes:
- It's strongly recommended to use readiness probes and PodDisruptionBudgets to reduce the impact of the node replacement operation.
- This operation is supported only with the
enhancedOKE clusters. - New nodes will be created within the same AD/FD as the ones they replace.
- Node cycle requests can be canceled but can't be reverted.
- When setting a high
node_cycling_max_surgevalue, check your tenancy compute limits to confirm availability of resources for the new worker nodes. - Compatible with the cluster_autoscaler. During node-cycling execution, the request to reduce node_pool size is rejected, and all the worker nodes within the cycled node_pool are annotated with
"cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled": "true"to prevent the termination of the newly created nodes. node_cycling_enabled = trueis incompatible with changes to the node_poolplacement_config(subnet_id, availability_domains, placement_fds, etc.)- If the
kubernetes_versionattribute is changed whenimage_type = custom, ensure a compatibleimage_idwith the new Kubernetes version is provided.
Usage
# Example worker pool node-cycle configuration.
worker_pools = {
cycled-node-pool = {
description = "Cycling nodes in a node_pool.",
size = 4,
node_cycling_enabled = true
node_cycling_max_surge = "25%"
node_cycling_max_unavailable = 0
node_cycling_mode = ["instance"] # An alternative value is boot_volume. Only a single mode is supported.
force_node_action = true // *true/false - Applicable when the node cycling mode is "boot_volume".
force_node_delete = true // *true/false - Applicable when the node cycling mode is "instance".
}
}
References
- oci_containerengine_node_pool
- Performing an In-Place Worker Node Update by Cycling Nodes in an Existing Node Pool
- Introducing On Demand Node Cycling for OCI Kubernetes Engine
Load Balancers
Using Dynamic and Flexible Load Balancers
When you create a service of type LoadBalancer, by default, an OCI Load Balancer with dynamic shape 100Mbps will be created.
.You can override this shape by using the {uri-oci-loadbalancer-annotations}[OCI Load Balancer Annotations]. In order to keep using the dynamic shape but change the available total bandwidth to 400Mbps, use the following annotation on your LoadBalancer service:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape: "400Mbps"
Configure flexible shape with bandwidth:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape: "flexible"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape-flex-min: 50
service.beta.kubernetes.io/oci-load-balancer-shape-flex-max: 200
References
Bastion
The bastion instance provides a public SSH entrypoint into the VCN from which resources in private subnets may be accessed - recommended to limit public IP usage and exposure.
The bastion host parameters concern: 0. whether you want to enable the bastion 0. from where you can access the bastion 0. the different parameters about the bastion host e.g. shape, image id etc.
Image
The OS image for the created bastion instance.
Recommended: Oracle Autonomous Linux 8.x
Example usage
create_bastion = true # *true/false
bastion_allowed_cidrs = [] # e.g. ["0.0.0.0/0"] to allow traffic from all sources
bastion_availability_domain = null # Defaults to first available
bastion_image_id = null # Ignored when bastion_image_type = "platform"
bastion_image_os = "Oracle Linux" # Ignored when bastion_image_type = "custom"
bastion_image_os_version = "8" # Ignored when bastion_image_type = "custom"
bastion_image_type = "platform" # platform/custom
bastion_nsg_ids = [] # Combined with created NSG when enabled in var.nsgs
bastion_public_ip = null # Ignored when create_bastion = true
bastion_type = "public" # *public/private
bastion_upgrade = false # true/*false
bastion_user = "opc"
bastion_shape = {
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 1,
memory = 4,
boot_volume_size = 50
baseline_ocpu_utilization = "100" # accepted values: 100/50/12.5. Supported only with burstable shapes.
}
Bastion: SSH
Command usage for ssh through the created bastion to the operator host is included in the module's output:
$ terraform output
cluster = {
"bastion_public_ip" = "138.0.0.1"
"ssh_to_operator" = "ssh -J opc@138.0.0.1 opc@10.0.0.16"
...
}
$ ssh -J opc@138.0.0.1 opc@10.0.0.16 kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
10.1.48.175 Ready node 7d10h v1.25.6
10.1.50.102 Ready node 3h12m v1.25.6
10.1.52.76 Ready node 7d10h v1.25.6
10.1.54.237 Ready node 5h41m v1.25.6
10.1.58.74 Ready node 5h22m v1.25.4
10.1.62.90 Ready node 3h12m v1.25.6
$ ssh -J opc@138.0.0.1 opc@10.1.54.237 systemctl status kubelet
● kubelet.service - Kubernetes Kubelet
Active: active (running) since Tue 2023-03-28 01:48:08 UTC; 5h 48min ago
...
Operator
The operator instance provides an optional environment within the VCN from which the OKE cluster can be managed.
The operator host parameters concern:
- whether you want to enable the operator
- from where you can access the operator
- the different parameters about the operator host e.g. shape, image id etc.
Example usage
create_operator = true # *true/false
operator_availability_domain = null
operator_cloud_init = []
operator_image_id = null # Ignored when operator_image_type = "platform"
operator_image_os = "Oracle Linux" # Ignored when operator_image_type = "custom"
operator_image_os_version = "8" # Ignored when operator_image_type = "custom"
operator_image_type = "platform"
operator_nsg_ids = []
operator_private_ip = null
operator_pv_transit_encryption = false # true/*false
operator_upgrade = false # true/*false
operator_user = "opc"
operator_volume_kms_key_id = null
operator_shape = {
shape = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex",
ocpus = 1,
memory = 4,
boot_volume_size = 50
baseline_ocpu_utilization = "100" # accepted values: 100/50/12.5. Supported only with burstable shapes.
}
Operator: Cloud-Init
Custom actions may be configured on instance startup in an number of ways depending on the use-case and preferences.
See also:
Cloud init configuration applied to the operator host:
operator_cloud_init = [
{
content = <<-EOT
runcmd:
- echo "Operator cloud_init using cloud-config"
EOT
content_type = "text/cloud-config",
},
{
content = "/path/to/file"
content_type = "text/cloud-boothook",
},
{
content = "<Base64-encoded content>"
content_type = "text/x-shellscript",
},
]
Operator: Identity
instance_principal
Instance_principal is an IAM service feature that enables instances to be authorized actors (or principals) to perform actions on service resources. Each compute instance has its own identity, and it authenticates using the certificates that are added to it. These certificates are automatically created, assigned to instances and rotated, preventing the need for you to distribute credentials to your hosts and rotate them.
Dynamic Groups group OCI instances as principal actors, similar to user groups. IAM policies can then be created to allow instances in these groups to make calls against OCI infrastructure services. For example, on the operator host, this permits kubectl to access the OKE cluster.
Any user who has access to the instance (who can SSH to the instance), automatically inherits the privileges granted to the instance. Before you enable this feature, ensure that you know who can access it, and that they should be authorized with the permissions you are granting to the instance.
By default, this feature is disabled. However, it is required at the time of cluster creation if you wish to enable KMS Integration or Extensions.
When you enable this feature, by default, the operator host will have privileges to all resources in the compartment. If you are enabling it for KMS Integration, the operator host will also have rights to create policies in the root tenancy.
Enabling instance_principal for the operator instance
instance_principal for the operator instance can be enabled or disabled at any time without impact on the operator or the cluster.
To enable this feature, specify the following to create of the necessary IAM policies, Dynamic Groups, and Matching Rules:
create_iam_resources = true
create_iam_operator_policy = "always"
To disable this feature, specify:
create_iam_operator_policy = "never"
Operator: SSH
Command usage for ssh through the created bastion to the operator host is included in the module's output:
$ terraform output
cluster = {
"bastion_public_ip" = "138.0.0.1"
"ssh_to_operator" = "ssh -J opc@138.0.0.1 opc@10.0.0.16"
...
}
$ ssh -J opc@138.0.0.1 opc@10.0.0.16 kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
10.1.48.175 Ready node 7d10h v1.25.6
10.1.50.102 Ready node 3h12m v1.25.6
10.1.52.76 Ready node 7d10h v1.25.6
10.1.54.237 Ready node 5h41m v1.25.6
10.1.58.74 Ready node 5h22m v1.25.4
10.1.62.90 Ready node 3h12m v1.25.6
Utilities
OCIR
NOTE: TODO Pending validation in 5.x
The auth token must first be manually created and stored in OCI Secret in Vault. It will subsequently be used to create a Kubernetes secret, which can then be used as an imagePullSecrets in a deployment. If you do not need to use private OCIR repositories, then leave the secret_id parameter empty.
The secret is created in the "default" namespace. To copy it to your namespace, use the following command:
kubectl --namespace=default get secret ocirsecret --export -o yaml | kubectl apply --namespace=<newnamespace> -f -
Creating a Secret
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Registry is a highly available private container registry service for storing and sharing container images within the same regions as the OKE Cluster. Use the following rules to determine if you need to create a Kubernetes Secret for OCIR:
- If your container repository is public, you do not need to create a secret.
- If your container repository is private, you need to create a secret before OKE can pull your images from the private repository.
If you plan on creating a Kubernetes Secret for OCIR, you must first create an Auth Token. Copy and temporarily save the value of the Auth Token.
You must then create a Secret in OCI Vault to store the value of the Auth Token in it.
Finally, assign the Secret OCID to secret_id in terraform.tfvars. Refer to {uri-terraform-options}#ocir[OCIR parameters] for other parameters to be set.
NOTE: Installing the Vertical Pod Autoscaler also requires installing the Metrics Server, so you need to enable that too.
Service account
NOTE: TODO Pending validation in 5.x
OKE now uses Kubeconfig v2 which means the default token has a limited lifespan. In order to allow CI/CD tools to deploy to OKE, a service account must be created.
Set the create_service_account = true and you can name the other parameters as appropriate:
create_service_account = true
service_account_name = "kubeconfigsa"
service_account_namespace = "kube-system"
service_account_cluster_role_binding = ""
KMS
The KMS integration parameters control whether OCI Key Management Service will be used for encrypting Kubernetes secrets and boot volumes/block volumes. Additionally, the bastion and operator hosts must be enabled as well as instance_principal on the operator.
OKE also supports enforcing the use of signed images. You can enforce the use of signed image using the following parameters:
use_signed_images = false
image_signing_keys = ["ocid1.key.oc1....", "ocid1.key.oc1...."]
Extensions
WARNING: The following options are provided as a reference for evaluation only, and may install software to the cluster that is not supported by or sourced from Oracle. These features should be enabled with caution as their operation is not guaranteed!
Gatekeeper
Usage
gatekeeper_install = true
gatekeeper_namespace = "kube-system"
gatekeeper_helm_version = "3.11.0"
gatekeeper_helm_values = {}
gatekeeper_helm_values_files = []
References
MPI Operator
Usage
mpi_operator_install = true
mpi_operator_namespace = "default"
mpi_operator_deployment = null // determined automatically for version by default
mpi_operator_version = "0.4.0"
References
Extensions: Standalone Cluster Autoscaler
Note: For the cluster autoscaler you should choose only one of the options:
- the stand-alone cluster-autoscaler deployment, using this extension
- the cluster-autoscaler add-on, using the addons.
Deployed using the cluster-autoscaler Helm chart with configuration from the worker_pools variable.
The module is using the oke.oraclecloud.com/cluster_autoscaler nodepool label to facilitate the understanding of how the Kubernetes cluster auto-scaler will interact with the node:
allowed- cluster-autoscaler deployment will be allowed to run on the nodes with this labelmanaged- cluster-autoscaler is managing this node (may terminate it if required)disabled- cluster-autoscaler will not run nor manage the node.
The following parameters may be added on each pool definition to enable management or scheduling of the cluster autoscaler:
allow_autoscaler: Enable scheduling of the cluster autoscaler deployment on a pool by adding a node label matching the deployment's nodeSelector (oke.oraclecloud.com/cluster_autoscaler: allowed), and an OCI defined tag for use with IAM tag-based policies granting access to the instances (${var.tag_namespace}.cluster_autoscaler: allowed).autoscale: Enable cluster autoscaler management of the pool by appending--nodes <nodepool-ocid>argument to the CMD of thecluster-autoscalercontainer. Nodes part of these nodepools will have the labeloke.oraclecloud.com/cluster_autoscaler: managedand an OCI defined tag${var.tag_namespace}.cluster_autoscaler: managed.min_size: Define the minimum scale of a pool managed by the cluster autoscaler. Defaults tosizewhen not provided.max_size: Define the maximum scale of a pool managed by the cluster autoscaler. Defaults tosizewhen not provided.
The cluster-autoscaler will manage the size of the nodepools with the attribute autoscale = true. To avoid the conflict between the actual size of a nodepool and the size defined in the terraform configuration files, you can add the ignore_initial_pool_size = true attribute to the nodepool definition in the worker_pools variable. This parameter will allow terraform to ignore the drift of the size parameter for the specific nodepool.
This setting is strongly recommended for nodepools configured with autoscale = true.
Example:
worker_pools = {
np-autoscaled = {
description = "Node pool managed by cluster autoscaler",
size = 2,
min_size = 1,
max_size = 3,
autoscale = true,
ignore_initial_pool_size = true # allows nodepool size drift
},
np-autoscaler = {
description = "Node pool with cluster autoscaler scheduling allowed",
size = 1,
allow_autoscaler = true,
},
}
For existing deployments is necessary to use the terraform state mv command.
Example for nodepool resource:
$ terraform plan
...
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# module.oke.module.workers[0].oci_containerengine_node_pool.tfscaled_workers["np-autoscaled"] will be destroyed
...
# module.oke.module.workers[0].oci_containerengine_node_pool.autoscaled_workers["np-autoscaled"] will be created
$ terraform state mv module.oke.module.workers[0].oci_containerengine_node_pool.tfscaled_workers[\"np-autoscaled\"] module.oke.module.workers[0].oci_containerengine_node_pool.autoscaled_workers[\"np-autoscaled\"]
Successfully moved 1 object(s).
$ terraform plan
...
No changes. Your infrastructure matches the configuration.
Example for instance_pool resource:
$ terraform state mv module.oke.module.workers[0].oci_core_instance_pool.tfscaled_workers[\"np-autoscaled\"] module.oke.module.workers[0].oci_core_instance_pool.autoscaled_workers[\"np-autoscaled\"]
Successfully moved 1 object(s).
Notes
Don't set allow_autoscaler and autoscale to true on the same pool. This will cause the cluster autoscaler pod to be unschedulable as the oke.oraclecloud.com/cluster_autoscaler: managed node label will override the oke.oraclecloud.com/cluster_autoscaler: allowed node label specified by the cluster autoscaler nodeSelector pod attribute.
Usage
cluster_autoscaler_install = true
cluster_autoscaler_namespace = "kube-system"
cluster_autoscaler_helm_version = "9.24.0"
cluster_autoscaler_helm_values = {}
cluster_autoscaler_helm_values_files = []
# Example worker pool configurations with cluster autoscaler
worker_pools = {
np-autoscaled = {
description = "Node pool managed by cluster autoscaler",
size = 2,
min_size = 1,
max_size = 3,
autoscale = true,
ignore_initial_pool_size = true
},
np-autoscaler = {
description = "Node pool with cluster autoscaler scheduling allowed",
size = 1,
allow_autoscaler = true,
},
}
References
- Cluster Autoscaler Helm chart
- Autoscaling Kubernetes Node Pools and Pods
- OCI Provider for Cluster Autoscaler
- Cluster Autoscaler FAQ
Extensions: Networking
WARNING: The following options are provided as a reference for evaluation only, and may install software to the cluster that is not supported by or sourced from Oracle. These features should be enabled with caution as their operation is not guaranteed!
Multus CNI
Usage
multus_install = true
multus_namespace = "network"
multus_daemonset_url = null // determined automatically for version by default
multus_version = "3.9.3"
References
Cilium CNI
Usage
cilium_install = true
cilium_reapply = false
cilium_namespace = "kube-system"
cilium_helm_version = "1.16.3"
cilium_helm_values = {}
cilium_helm_values_files = []
Cillium is a eBPF based CNI for Kubernetes that can be configured on OKE clusters.
The OKE cluster should be initially configured to run flannel.
On enhanced clusters we can use the cluster-addons module to remove flannel extension and kube-proxy (Optional) at cluster creation.
cluster_addons_to_remove = {
Flannel = {
remove_k8s_resources = true
},
KubeProxy = {
remove_k8s_resources = true
}
}
If you want to use cilium as kube-proxy replacement, you can use the following helm_values:
cilium_helm_values = {
kubeProxyReplacement = true
}
For the basic clusters you can add the following label to the worker nodes to prevent flannel pods from being scheduled:
oci.oraclecloud.com/custom-k8s-networking=true
If you want to override and of the default values(listed below) you can use the cilium_helm_values variable:
"annotateK8sNode": true
"cluster":
"id": 1
"name": "oke-${var.state_id}"
"clustermesh":
"apiserver":
"kvstoremesh":
"enabled": false
"useAPIServer": false
"cni":
"exclusive": true
"install": true
"hubble":
"metrics":
"dashboards":
"enabled": false
"relay":
"enabled": true
"ui":
"enabled": true
"installNoConntrackIptablesRules": false
"ipam":
"mode": "kubernetes"
"k8s":
"requireIPv4PodCIDR": true
"k8sServiceHost": "${var.cluster_private_endpoint}"
"k8sServicePort": "6443"
"kubeProxyReplacement": false
"operator":
"prometheus":
"enabled": false
"pmtuDiscovery":
"enabled": true
"rollOutCiliumPods": true
"tunnelProtocol": "vxlan"
Notes:
-
Tested with OKE version
v1.29.1and the worker nodes running:Oracle-Linux-8.9-2024.05.29-0-OKE-1.29.1-707. -
In case the
hubble-relayandhubble-uipods fail to start, run the following commands:
kubectl delete pod --namespace kube-system -l k8s-app=kube-dns
kubectl delete pod --namespace kube-system -l k8s-app=hubble-relay
kubectl delete pod --namespace kube-system -l k8s-app=hubble-ui
kubectl delete pod --namespace kube-system -l k8s-app=kube-dns-autoscaler
References
Whereabouts IPAM plugin
Usage
whereabouts_install = true
whereabouts_namespace = "network"
whereabouts_daemonset_url = null // determined automatically for version by default
whereabouts_version = "master"
References
SR-IOV Device plugin
Usage
sriov_device_plugin_install = true
sriov_device_plugin_namespace = "network"
sriov_device_plugin_daemonset_url = null // determined automatically for version by default
sriov_device_plugin_version = "master"
References
SR-IOV CNI plugin
Usage
sriov_cni_plugin_install = true
sriov_cni_plugin_namespace = "network"
sriov_cni_plugin_daemonset_url = null // determined automatically for version by default
sriov_cni_plugin_version = "master"
References
RDMA CNI plugin
Usage
rdma_cni_plugin_install = true
rdma_cni_plugin_namespace = "network"
rdma_cni_plugin_daemonset_url = null // determined automatically for version by default
rdma_cni_plugin_version = "master"
References
Extensions: Monitoring
WARNING: The following options are provided as a reference for evaluation only, and may install software to the cluster that is not supported by or sourced from Oracle. These features should be enabled with caution as their operation is not guaranteed!
Metrics Server
Usage
metrics_server_install = true
metrics_server_namespace = "metrics"
metrics_server_daemonset_url = null // determined automatically for version by default
metrics_server_version = "master"
References
Prometheus
Usage
prometheus_install = true
prometheus_reapply = false
prometheus_namespace = "metrics"
prometheus_helm_version = "45.2.0"
prometheus_helm_values = {}
prometheus_helm_values_files = []
References
DCGM Exporter
Usage
dcgm_exporter_install = true
dcgm_exporter_reapply = false
dcgm_exporter_namespace = "metrics"
dcgm_exporter_helm_version = "3.1.5"
dcgm_exporter_helm_values = {}
dcgm_exporter_helm_values_files = []
References
Upgrading
TODO Update content
This section documents how to upgrade the OKE cluster using this project. At a high level, upgrading the OKE cluster is fairly straightforward:
- Upgrade the control plane nodes
- Upgrade the worker nodes using either {uri-upgrade-oke}[in-place or out-of-place] approach
These steps must be performed in order.
Prerequisites
For in-place upgrade:
- Enhanced cluster
For out-of-place upgrade:
- Bastion host is created
- Operator host is created
- instance_principal is enabled on operator
Upgrading the control plane nodes
Locate your kubernetes_version in your Terraform variable file and change:
kubernetes_version = "v1.22.5"
to
kubernetes_version = "v1.23.4"
Run terraform apply. This will upgrade the control plane nodes. You can verify this in the OCI Console.
If you have modified the default resources e.g. security lists, you will need to use a targeted apply:
terraform apply --target=module.oke.k8s_cluster
Upgrading the worker nodes using the in-place method
In-place worker node upgrade is performed using the node_pool node_cycle operation.
Set node_cycling_enabled for the existing node_pools you want to upgrade and control the node replacement strategy using: node_cycling_max_surge and node_cycling_max_unavailable.
worker_pools = {
cycled-node-pool = {
description = "Cycling nodes in a node_pool.",
size = 2,
node_cycling_enabled = true
node_cycling_max_surge = 1
node_cycling_max_unavailable = 0
}
}
By default, the node_pools are using the same Kubernetes version as the control plane (defined in the kubernetes_version variable).
Note: You can override each node_pool Kubernetes version via the kubernetes_version attribute in the worker_pools variable.
kubernetes_version = "v1.26.7" # control plane Kubernetes version (used by default for the node_pools).
worker_pools = {
cycled-node-pool = {
description = "Cycling nodes in a node_pool.",
size = 2,
kubernetes_version = "v1.26.2" # override the default Kubernetes version
}
}
Worker node image compatibility
If the node_pool is configured to use a custom worker node image (image_type = custom), make sure that the worker ndoe image referenced in the image_id attribute of the worker_pools is compatible with the new kubernetes_version.
kubernetes_version = "v1.26.7" # control plane Kubernetes version (used by default for the node_pools).
worker_pools = {
cycled-node-pool = {
description = "Cycling nodes in a node_pool.",
size = 2,
image_type = "custom",
image_id = "ocid1.image..."
}
}
Note: A new image_id, compatible with the node_pool kubernetes_version is automatically configured when image_type is not configured for the node_pool or set to the values ("oke" or "platform").
Upgrading the worker nodes using the out-of-place method
Add new node pools
Add a new node pool in your list of node pools e.g. change:
worker_pools = {
np1 = ["VM.Standard.E2.2", 7, 50]
np2 = ["VM.Standard2.8", 5, 50]
}
to
worker_pools = {
np1 = ["VM.Standard.E2.2", 7, 50]
np2 = ["VM.Standard2.8", 5, 50]
np3 = ["VM.Standard.E2.2", 7, 50]
np4 = ["VM.Standard2.8", 5, 50]
}
and run terraform apply again. (See note above about targeted apply). If you are using Kubernetes labels for your existing applications, you will need to ensure the new node pools also have the same labels. Refer to the terraform.tfvars.example file for the format to specify the labels.
When node pools 3 and 4 are created, they will be created with the newer cluster version of Kubernetes. Since you have already upgrade your cluster to v1.23.4, node pools 3 and 4 will be running Kubernetes v1.23.4.
Drain older nodepools
Set upgrade_nodepool=true. This will instruct the OKE cluster that some node pools will be drained.
Provide the list of node pools to drain. This should usually be only the old node pools. You don't need to upgrade all the node pools at once.
worker_pools_to_drain = [ "np1", "np2"]
Rerun terraform apply (see note above about targeted apply).
Delete node pools with older Kubernetes version
When you are ready, you can now delete the old node pools by removing them from the list of node pools:
worker_pools = {
np3 = ["VM.Standard.E2.2", 7, 50]
np4 = ["VM.Standard2.8", 5, 50]
}
Rerun terraform apply. This completes the upgrade process. Now, set upgrade_nodepool = false to prevent draining from current nodes by mistake.
Deploy the OKE Terraform Module
Prerequisites
- Required Keys and OCIDs
- Required IAM policies
git,sshclient to run locally- Terraform
>= 1.2.0to run locally
Provisioning from an OCI Resource Manager Stack
Network
Network resources configured for an OKE cluster.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Cluster
An OKE-managed Kubernetes cluster.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- core_network_security_group
- core_network_security_group_security_rule
- core_instance (operator)
- containerengine_cluster
Node Pool
A standard OKE-managed pool of worker nodes with enhanced feature support.
Configured with mode = "node-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "node-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
You can set the image_type attribute to one of the following values:
oke(default)platformcustom.
When the image_type is equal to oke or platform there is a high risk for the node-pool image to be updated on subsequent terraform apply executions because the module is using a datasource to fetch the latest images available.
To avoid this situation, you can set the image_type to custom and the image_id to the OCID of the image you want to use for the node-pool.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Virtual Node Pool
An OKE-managed Virtual Node Pool.
Configured with mode = "virtual-node-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "virtual-node-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
Instance
A set of self-managed Compute Instances for custom user-provisioned worker nodes not managed by an OCI pool, but individually by Terraform.
Configured with mode = "instance" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "instance" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance
Instance Pool
A self-managed Compute Instance Pool for custom user-provisioned worker nodes.
Configured with mode = "instance-pool" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "instance-pool" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance_configuration
- core_instance_pool
Cluster Network
A self-managed HPC Cluster Network.
Configured with mode = "cluster-network" on a worker_pools entry, or with worker_pool_mode = "cluster-network" to use as the default for all pools unless otherwise specified.
The following resources may be created depending on provided configuration:
- identity_dynamic_group (workers)
- identity_policy (JoinCluster)
- core_instance_configuration
- core_cluster_network
Reference
Inputs
The module supports the following configuration for created resources:
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| allow_rules_cp | A map of additional rules to allow traffic for the OKE control plane. | any | {} | no |
| allow_rules_internal_lb | A map of additional rules to allow incoming traffic for internal load balancers. | any | {} | no |
| allow_rules_pods | A map of additional rules to allow traffic for the pods. | any | {} | no |
| allow_rules_public_lb | A map of additional rules to allow incoming traffic for public load balancers. | any | {} | no |
| allow_rules_workers | A map of additional rules to allow traffic for the workers. | any | {} | no |
| cilium_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/helm/latest/docs/data-sources/template. | any | {} | no |
| cluster_addons | Map with cluster addons that should be enabled. See ClusterAddon documentation for the supported configuration of each addon. | any | {} | no |
| cluster_addons_to_remove | Map with cluster addons not created by Terraform that should be removed. This operation is performed using oci-cli and requires the operator host to be deployed. | any | {} | no |
| defined_tags | Defined tags to be applied to created resources. Must already exist in the tenancy. | any | { "bastion": {}, "cluster": {}, "iam": {}, "network": {}, "operator": {}, "persistent_volume": {}, "service_lb": {}, "workers": {} } | no |
| drg_attachments | DRG attachment configurations. | any | {} | no |
| freeform_tags | Freeform tags to be applied to created resources. | any | { "bastion": {}, "cluster": {}, "iam": {}, "network": {}, "operator": {}, "persistent_volume": {}, "service_lb": {}, "workers": {} } | no |
| oidc_token_authentication_config | The properties that configure OIDC token authentication in kube-apiserver. See OIDC Token Authentication configuration documentation. | any | {} | no |
| worker_pools | Tuple of OKE worker pools where each key maps to the OCID of an OCI resource, and value contains its definition. | any | {} | no |
| allow_bastion_cluster_access | Whether to allow access to the Kubernetes cluster endpoint from the bastion host. | bool | false | no |
| allow_node_port_access | Whether to allow access from worker NodePort range to load balancers. | bool | false | no |
| allow_pod_internet_access | Allow pods to egress to internet. Ignored when cni_type != 'npn'. | bool | true | no |
| allow_short_container_image_names | Whether to allow short container image names for K8s version >= 1.34.0. See CRI-O pull request for more information. | bool | false | no |
| allow_worker_internet_access | Allow worker nodes to egress to internet. Required if container images are in a registry other than OCIR. | bool | true | no |
| allow_worker_ssh_access | Whether to allow SSH access to worker nodes. | bool | false | no |
| argocd_install | Whether to deploy the Argocd Helm chart. See https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| assign_dns | Whether to assign DNS records to created instances or disable DNS resolution of hostnames in the VCN. | bool | true | no |
| assign_public_ip_to_control_plane | Whether to assign a public IP address to the API endpoint for public access. Requires the control plane subnet to be public to assign a public IP address. | bool | false | no |
| bastion_await_cloudinit | Whether to block until successful connection to bastion and completion of cloud-init. | bool | true | no |
| bastion_is_public | Whether to create allocate a public IP and subnet for the created bastion host. | bool | true | no |
| bastion_upgrade | Whether to upgrade bastion packages after provisioning. | bool | false | no |
| cilium_install | Whether to deploy the Cilium Helm chart. May only be enabled when cni_type = 'flannel'. See https://docs.cilium.io. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| cilium_reapply | Whether to force reapply of the chart when no changes are detected, e.g. with state modified externally. | bool | false | no |
| cluster_autoscaler_install | Whether to deploy the Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler Helm chart. See kubernetes/autoscaler. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| control_plane_is_public | Whether the Kubernetes control plane endpoint should be allocated a public IP address to enable access over public internet. | bool | false | no |
| create_bastion | Whether to create a bastion host. | bool | true | no |
| create_cluster | Whether to create the OKE cluster and dependent resources. | bool | true | no |
| create_drg | Whether to create a Dynamic Routing Gateway and attach it to the VCN. | bool | false | no |
| create_iam_defined_tags | Whether to create defined tags used for IAM policy and tracking. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | bool | false | no |
| create_iam_resources | Whether to create IAM dynamic groups, policies, and tags. Resources for components may be controlled individually with 'create_iam_*' variables when enabled. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | bool | false | no |
| create_iam_tag_namespace | Whether to create a namespace for defined tags used for IAM policy and tracking. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | bool | false | no |
| create_operator | Whether to create an operator server in a private subnet. | bool | true | no |
| create_service_account | Wether to create a service account or not. | bool | false | no |
| create_vcn | Whether to create a Virtual Cloud Network. | bool | true | no |
| dcgm_exporter_install | Whether to deploy the DCGM exporter Helm chart. See DCGM-Exporter. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| dcgm_exporter_reapply | Whether to force reapply of the Helm chart when no changes are detected, e.g. with state modified externally. | bool | false | no |
| enable_ipv6 | Whether to create a dual-stack (IPv4/IPv6) cluster. | bool | false | no |
| enable_waf | Whether to enable WAF monitoring of load balancers. | bool | false | no |
| gatekeeper_install | Whether to deploy the Gatekeeper Helm chart. See https://github.com/open-policy-agent/gatekeeper. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| lockdown_default_seclist | Whether to remove all default security rules from the VCN Default Security List. | bool | true | no |
| metrics_server_install | Whether to deploy the Kubernetes Metrics Server Helm chart. See kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| mpi_operator_install | Whether to deploy the MPI Operator. See kubeflow/mpi-operator. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| multus_install | Whether to deploy Multus. See k8snetworkplumbingwg/multus-cni. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| oidc_discovery_enabled | Whether the cluster has OIDC Discovery enabled. See OIDC Discovery configuration documentation. | bool | false | no |
| oidc_token_auth_enabled | Whether the cluster has OIDC Auth Config enabled. | bool | false | no |
| operator_await_cloudinit | Whether to block until successful connection to operator and completion of cloud-init. | bool | true | no |
| operator_install_helm | Whether to install Helm on the created operator host. | bool | true | no |
| operator_install_helm_from_repo | Whether to install Helm from the repo on the created operator host. | bool | false | no |
| operator_install_istioctl | Whether to install istioctl on the created operator host. | bool | false | no |
| operator_install_k8sgpt | Whether to install k8sgpt on the created operator host. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| operator_install_k9s | Whether to install k9s on the created operator host. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| operator_install_kubectl_from_repo | Whether to install kubectl from the repo on the created operator host. | bool | true | no |
| operator_install_kubectx | Whether to install kubectx/kubens on the created operator host. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | true | no |
| operator_install_oci_cli_from_repo | Whether to install OCI from repo on the created operator host. | bool | false | no |
| operator_install_stern | Whether to install stern on the created operator host. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| operator_pv_transit_encryption | Whether to enable in-transit encryption for the data volume's paravirtualized attachment. | bool | false | no |
| operator_upgrade | Whether to upgrade operator packages after provisioning. | bool | false | no |
| output_detail | Whether to include detailed output in state. | bool | false | no |
| prometheus_install | Whether to deploy the Prometheus Helm chart. See https://github.com/prometheus-community/helm-charts/tree/main/charts/kube-prometheus-stack. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| prometheus_reapply | Whether to force reapply of the Prometheus Helm chart when no changes are detected, e.g. with state modified externally. | bool | false | no |
| rdma_cni_plugin_install | Whether to deploy the SR-IOV CNI Plugin. See <a href=https://github.com/openshift/sriov-cni. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| sriov_cni_plugin_install | Whether to deploy the SR-IOV CNI Plugin. See <a href=https://github.com/openshift/sriov-cni. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| sriov_device_plugin_install | Whether to deploy the SR-IOV Network Device Plugin. See k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-network-device-plugin. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| use_defined_tags | Whether to apply defined tags to created resources for IAM policy and tracking. | bool | false | no |
| use_signed_images | Whether to enforce the use of signed images. If set to true, at least 1 RSA key must be provided through image_signing_keys. | bool | false | no |
| use_stateless_rules | (experimental) Create NSGs with stateless rules instead of the default stateful rules. | bool | false | no |
| vcn_enable_ipv6_gua | Whether to enable IPv6 GUA when IPv6 is enabled. | bool | true | no |
| whereabouts_install | Whether to deploy the MPI Operator. See k8snetworkplumbingwg/whereabouts. NOTE: Provided only as a convenience and not supported by or sourced from Oracle - use at your own risk. | bool | false | no |
| worker_disable_default_cloud_init | Whether to disable the default OKE cloud init and only use the cloud init explicitly passed to the worker pool in 'worker_cloud_init'. | bool | false | no |
| worker_drain_delete_local_data | Whether to accept removal of data stored locally on draining worker pools. See kubectl drain for more information. | bool | true | no |
| worker_drain_ignore_daemonsets | Whether to ignore DaemonSet-managed Pods when draining worker pools. See kubectl drain for more information. | bool | true | no |
| worker_is_public | Whether to provision workers with public IPs allocated by default when unspecified on a pool. It should be true when creating dual-stack clusters. | bool | false | no |
| worker_legacy_imds_endpoints_disabled | Whether to disable requests to the IMDSv1 endpoint and only allow requests to the IMDSv2 endpoint. See Instance Metadata for more information. | bool | false | no |
| worker_pv_transit_encryption | Whether to enable in-transit encryption for the data volume's paravirtualized attachment by default when unspecified on a pool. | bool | false | no |
| internet_gateway_route_rules | (Updatable) List of routing rules to add to Internet Gateway Route Table. | list(map(string)) | null | no |
| nat_gateway_route_rules | (Updatable) List of routing rules to add to NAT Gateway Route Table. | list(map(string)) | null | no |
| operator_cloud_init | List of maps containing cloud init MIME part configuration for operator host. See https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/template/latest/docs/data-sources/cloudinit_config.html#part for expected schema of each element. | list(map(string)) | [] | no |
| worker_cloud_init | List of maps containing cloud init MIME part configuration for worker nodes. Merged with pool-specific definitions. See https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/template/latest/docs/data-sources/cloudinit_config.html#part for expected schema of each element. | list(map(string)) | [] | no |
| argocd_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| bastion_allowed_cidrs | A list of CIDR blocks to allow SSH access to the bastion host. NOTE: Default is empty i.e. no access permitted. Allow access from anywhere with '0.0.0.0/0'. | list(string) | [] | no |
| bastion_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security group (NSG) IDs for bastion security. | list(string) | [] | no |
| cilium_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| cluster_autoscaler_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| control_plane_allowed_cidrs | The list of CIDR blocks from which the control plane can be accessed. | list(string) | [] | no |
| dcgm_exporter_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| gatekeeper_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| metrics_server_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| oke_ip_families | Override the ip_families attribute for the OKE cluster. Supported values: ['IPv4'] or ['IPV4', 'IPv6'] | list(string) | [] | no |
| operator_nsg_ids | An optional and updatable list of network security groups that the operator will be part of. | list(string) | [] | no |
| pod_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security group (NSG) IDs for pod security. Combined with 'pod_nsg_ids' specified on each pool. | list(string) | [] | no |
| prometheus_helm_values_files | Paths to a local YAML files with Helm chart values (as with helm install -f which supports multiple). Generate with defaults using helm show values [CHART] [flags]. | list(string) | [] | no |
| vcn_cidrs | The list of IPv4 CIDR blocks the VCN will use. | list(string) | [ "10.0.0.0/16" ] | no |
| vcn_ipv6_ula_cidrs | IPv6 ULA CIDR blocks to be used for the VCN. | list(string) | [] | no |
| worker_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security group (NSG) IDs for node security. Combined with 'nsg_ids' specified on each pool. | list(string) | [] | no |
| bastion_shape | The shape of bastion instance. Baseline OCPU utilization can be used to provision burstable shapes. | map(any) | { "baseline_ocpu_utilization": 100, "boot_volume_size": 50, "memory": 4, "ocpus": 1, "shape": "VM.Standard.E4.Flex" } | no |
| local_peering_gateways | Map of Local Peering Gateways to attach to the VCN. | map(any) | null | no |
| operator_shape | Shape of the created operator instance. Baseline OCPU utilization can be used to provision burstable shapes. | map(any) | { "baseline_ocpu_utilization": 100, "boot_volume_size": 50, "memory": 4, "ocpus": 1, "shape": "VM.Standard.E4.Flex" } | no |
| remote_peering_connections | Map of parameters to add and optionally to peer to remote peering connections. Key-only items represent local acceptors and no peering attempted; items containing key and values represent local requestor and must have the OCID and region of the remote acceptor to peer to | map(any) | {} | no |
| service_accounts | Map of service accounts and associated parameters. | map(any) | { "kubeconfigsa": { "sa_cluster_role": "cluster-admin", "sa_cluster_role_binding": "kubeconfigsa-crb", "sa_name": "kubeconfigsa", "sa_namespace": "kube-system" } } | no |
| worker_compute_clusters | Whether to create compute clusters shared by nodes across multiple worker pools enabled for 'compute-cluster'. | map(any) | {} | no |
| worker_preemptible_config | Default preemptible Compute configuration when unspecified on a pool. See Preemptible Worker Nodes for more information. | map(any) | { "enable": false, "is_preserve_boot_volume": false } | no |
| worker_shape | Default shape of the created worker instance when unspecified on a pool. | map(any) | { "boot_volume_size": 50, "boot_volume_vpus_per_gb": 10, "memory": 16, "ocpus": 2, "shape": "VM.Standard.E4.Flex" } | no |
| subnets | Configuration for standard subnets. The 'create' parameter of each entry defaults to 'auto', creating subnets when other enabled components are expected to utilize them, and may be configured with 'never' or 'always' to force disabled/enabled. | map(object({ create = optional(string) id = optional(string) newbits = optional(string) netnum = optional(string) cidr = optional(string) display_name = optional(string) dns_label = optional(string) ipv6_cidr = optional(string) })) | { "bastion": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 0", "newbits": 13 }, "cp": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 2", "newbits": 13 }, "int_lb": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 3", "newbits": 11 }, "operator": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 1", "newbits": 13 }, "pods": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 6", "newbits": 2 }, "pub_lb": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 4", "newbits": 11 }, "workers": { "ipv6_cidr": "8, 5", "newbits": 4 } } | no |
| nsgs | Configuration for standard network security groups (NSGs). The 'create' parameter of each entry defaults to 'auto', creating NSGs when other enabled components are expected to utilize them, and may be configured with 'never' or 'always' to force disabled/enabled. | map(object({ create = optional(string) id = optional(string) })) | { "bastion": {}, "cp": {}, "int_lb": {}, "operator": {}, "pods": {}, "pub_lb": {}, "workers": {} } | no |
| argocd_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See data.helm_template. | map(string) | {} | no |
| bastion_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| bastion_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| cluster_autoscaler_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See data.helm_template. | map(string) | {} | no |
| cluster_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| cluster_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| dcgm_exporter_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See data.helm_template. | map(string) | {} | no |
| gatekeeper_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See data.helm_template. | map(string) | {} | no |
| iam_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| iam_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| metrics_server_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See data.helm_template. | map(string) | {} | no |
| network_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| network_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| operator_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| operator_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| persistent_volume_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| persistent_volume_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| prometheus_helm_values | Map of individual Helm chart values. See data.helm_template. | map(string) | {} | no |
| service_lb_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| service_lb_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| worker_node_labels | Default worker node labels. Merged with labels defined on each pool. | map(string) | {} | no |
| worker_node_metadata | Map of additional worker node instance metadata. Merged with metadata defined on each pool. | map(string) | {} | no |
| workers_defined_tags | Defined tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| workers_freeform_tags | Freeform tags applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| max_pods_per_node | The default maximum number of pods to deploy per node when unspecified on a pool. Absolute maximum is 110. Ignored when when cni_type != 'npn'. | number | 31 | no |
| worker_drain_timeout_seconds | The length of time to wait before giving up on draining nodes in a pool. See kubectl drain for more information. | number | 900 | no |
| worker_pool_size | Default size for worker pools when unspecified on a pool. | number | 0 | no |
| agent_config | Default agent_config for self-managed worker pools created with mode: 'instance', 'instance-pool', or 'cluster-network'. See <a href=https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/api/#/en/iaas/20160918/datatypes/InstanceAgentConfig for more information. | object({ are_all_plugins_disabled = bool, is_management_disabled = bool, is_monitoring_disabled = bool, plugins_config = map(string), }) | null | no |
| platform_config | Default platform_config for self-managed worker pools created with mode: 'instance', 'instance-pool', or 'cluster-network'. See PlatformConfig for more information. | object({ type = optional(string), are_virtual_instructions_enabled = optional(bool), is_access_control_service_enabled = optional(bool), is_input_output_memory_management_unit_enabled = optional(bool), is_measured_boot_enabled = optional(bool), is_memory_encryption_enabled = optional(bool), is_secure_boot_enabled = optional(bool), is_symmetric_multi_threading_enabled = optional(bool), is_trusted_platform_module_enabled = optional(bool), numa_nodes_per_socket = optional(number), percentage_of_cores_enabled = optional(bool), }) | null | no |
| backend_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security groups (NSG) ids for the LB backends. Used when the service rule management mode is set to NSG via annotations. See Security Rule Management Options for Load Balancers and Network Load Balancers for more information. | set(string) | [] | no |
| control_plane_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security groups (NSG) ids for the cluster endpoint. | set(string) | [] | no |
| image_signing_keys | A list of KMS key ids used by the worker nodes to verify signed images. The keys must use RSA algorithm. | set(string) | [] | no |
| api_fingerprint | Fingerprint of the API private key to use with OCI API. | string | null | no |
| api_private_key | The contents of the private key file to use with OCI API, optionally base64-encoded. This takes precedence over private_key_path if both are specified in the provider. | string | null | no |
| api_private_key_password | The corresponding private key password to use with the api private key if it is encrypted. | string | null | no |
| api_private_key_path | The path to the OCI API private key. | string | null | no |
| argocd_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "8.1.2" | no |
| argocd_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "argocd" | no |
| await_node_readiness | Optionally block completion of Terraform apply until one/all worker nodes become ready. | string | "none" | no |
| bastion_availability_domain | The availability domain for bastion placement. Defaults to first available. | string | null | no |
| bastion_image_id | Image ID for created bastion instance. | string | null | no |
| bastion_image_os | Bastion image operating system name when bastion_image_type = 'platform'. | string | "Oracle Autonomous Linux" | no |
| bastion_image_os_version | Bastion image operating system version when bastion_image_type = 'platform'. | string | "8" | no |
| bastion_image_type | Whether to use a platform or custom image for the created bastion instance. When custom is set, the bastion_image_id must be specified. | string | "platform" | no |
| bastion_public_ip | The IP address of an existing bastion host, if create_bastion = false. | string | null | no |
| bastion_user | User for SSH access through bastion host. | string | "opc" | no |
| bastion_volume_kms_key_id | The OCID of the OCI KMS key to assign as the master encryption key for the bastion host boot volume. | string | null | no |
| cilium_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "1.16.3" | no |
| cilium_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "kube-system" | no |
| cluster_autoscaler_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "9.24.0" | no |
| cluster_autoscaler_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "kube-system" | no |
| cluster_ca_cert | Base64+PEM-encoded cluster CA certificate for unmanaged instance pools. Determined automatically when 'create_cluster' = true or 'cluster_id' is provided. | string | null | no |
| cluster_dns | Cluster DNS resolver IP address. Determined automatically when not set (recommended). | string | null | no |
| cluster_id | An existing OKE cluster OCID when create_cluster = false. | string | null | no |
| cluster_kms_key_id | The id of the OCI KMS key to be used as the master encryption key for Kubernetes secrets encryption. | string | "" | no |
| cluster_name | The name of oke cluster. | string | "oke" | no |
| cluster_type | The cluster type. See Working with Enhanced Clusters and Basic Clusters for more information. | string | "basic" | no |
| cni_type | The CNI for the cluster: 'flannel' or 'npn'. See Pod Networking. | string | "flannel" | no |
| compartment_id | The compartment id where resources will be created. | string | null | no |
| compartment_ocid | A compartment OCID automatically populated by Resource Manager. | string | null | no |
| config_file_profile | The profile within the OCI config file to use. | string | "DEFAULT" | no |
| create_iam_autoscaler_policy | Whether to create an IAM dynamic group and policy rules for Cluster Autoscaler management. Depends on configuration of associated component when set to 'auto'. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | string | "auto" | no |
| create_iam_kms_policy | Whether to create an IAM dynamic group and policy rules for cluster autoscaler. Depends on configuration of associated components when set to 'auto'. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | string | "auto" | no |
| create_iam_operator_policy | Whether to create an IAM dynamic group and policy rules for operator access to the OKE control plane. Depends on configuration of associated components when set to 'auto'. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | string | "auto" | no |
| create_iam_worker_policy | Whether to create an IAM dynamic group and policy rules for self-managed worker nodes. Depends on configuration of associated components when set to 'auto'. Ignored when 'create_iam_resources' is false. | string | "auto" | no |
| current_user_ocid | A user OCID automatically populated by Resource Manager. | string | null | no |
| dcgm_exporter_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "3.1.5" | no |
| dcgm_exporter_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "metrics" | no |
| drg_compartment_id | Compartment for the DRG resource. Can be used to override network_compartment_id. | string | null | no |
| drg_display_name | (Updatable) Name of the created Dynamic Routing Gateway. Does not have to be unique. Defaults to 'oke' suffixed with the generated Terraform 'state_id' value. | string | null | no |
| drg_id | ID of an external created Dynamic Routing Gateway to be attached to the VCN. | string | null | no |
| gatekeeper_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "3.11.0" | no |
| gatekeeper_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "kube-system" | no |
| home_region | The tenancy's home region. Required to perform identity operations. | string | null | no |
| ig_route_table_id | Optional ID of existing internet gateway route table in VCN. | string | null | no |
| igw_ngw_mixed_route_id | Optional ID of the existing route table in VCN using IGW for IPv6 and NGW for IPv4. | string | null | no |
| internet_gateway_id | Optional ID of existing Internet gateway in VCN. | string | null | no |
| kubeproxy_mode | The mode in which to run kube-proxy when unspecified on a pool. | string | "iptables" | no |
| kubernetes_version | The version of kubernetes to use when provisioning OKE or to upgrade an existing OKE cluster to. | string | "v1.34.2" | no |
| load_balancers | The type of subnets to create for load balancers. | string | "both" | no |
| metrics_server_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "3.8.3" | no |
| metrics_server_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "metrics" | no |
| mpi_operator_deployment_url | The URL path to the manifest. Leave unset for tags of kubeflow/mpi-operator using mpi_operator_version. | string | null | no |
| mpi_operator_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "default" | no |
| mpi_operator_version | Version to install. Ignored when an explicit value for mpi_operator_deployment_url is provided. | string | "0.4.0" | no |
| multus_daemonset_url | The URL path to the Multus manifest. Leave unset for tags of k8snetworkplumbingwg/multus-cni using multus_version. | string | null | no |
| multus_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "network" | no |
| multus_version | Version of Multus to install. Ignored when an explicit value for multus_daemonset_url is provided. | string | "3.9.3" | no |
| nat_gateway_id | Optional ID of existing NAT gateway in VCN. | string | null | no |
| nat_gateway_public_ip_id | OCID of reserved IP address for NAT gateway. The reserved public IP address needs to be manually created. | string | null | no |
| nat_route_table_id | Optional ID of existing NAT gateway route table in VCN. | string | null | no |
| network_compartment_id | The compartment id where network resources will be created. | string | null | no |
| ocir_email_address | The email address used for the Oracle Container Image Registry (OCIR). | string | null | no |
| ocir_secret_id | The OCI Vault secret ID for the OCIR authentication token. | string | null | no |
| ocir_secret_name | The name of the Kubernetes secret to be created with the OCIR authentication token. | string | "ocirsecret" | no |
| ocir_secret_namespace | The Kubernetes namespace in which to create the OCIR secret. | string | "default" | no |
| ocir_username | A username with access to the OCI Vault secret for OCIR access. Required when 'ocir_secret_id' is provided. | string | null | no |
| operator_availability_domain | The availability domain for FSS placement. Defaults to first available. | string | null | no |
| operator_image_id | Image ID for created operator instance. | string | null | no |
| operator_image_os | Operator image operating system name when operator_image_type = 'platform'. | string | "Oracle Linux" | no |
| operator_image_os_version | Operator image operating system version when operator_image_type = 'platform'. | string | "8" | no |
| operator_image_type | Whether to use a platform or custom image for the created operator instance. When custom is set, the operator_image_id must be specified. | string | "platform" | no |
| operator_private_ip | The IP address of an existing operator host. Ignored when create_operator = true. | string | null | no |
| operator_user | User for SSH access to operator host. | string | "opc" | no |
| operator_volume_kms_key_id | The OCID of the OCI KMS key to assign as the master encryption key for the operator host boot volume. | string | null | no |
| pods_cidr | The CIDR range used for IP addresses by the pods. A /16 CIDR is generally sufficient. This CIDR should not overlap with any subnet range in the VCN (it can also be outside the VCN CIDR range). Ignored when cni_type = 'npn'. | string | "10.244.0.0/16" | no |
| preferred_load_balancer | The preferred load balancer subnets that OKE will automatically choose when creating a load balancer. Valid values are 'public' or 'internal'. If 'public' is chosen, the value for load_balancers must be either 'public' or 'both'. If 'private' is chosen, the value for load_balancers must be either 'internal' or 'both'. NOTE: Service annotations for internal load balancers must still be specified regardless of this setting. See Load Balancer Annotations for more information. | string | "public" | no |
| prometheus_helm_version | Version of the Helm chart to install. List available releases using helm search repo [keyword] --versions. | string | "45.2.0" | no |
| prometheus_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "metrics" | no |
| rdma_cni_plugin_daemonset_url | The URL path to the manifest. Leave unset for tags of <a href=https://github.com/openshift/sriov-cni using rdma_cni_plugin_version. | string | null | no |
| rdma_cni_plugin_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "network" | no |
| rdma_cni_plugin_version | Version to install. Ignored when an explicit value for rdma_cni_plugin_daemonset_url is provided. | string | "master" | no |
| region | The OCI region where OKE resources will be created. | string | "us-ashburn-1" | no |
| services_cidr | The CIDR range used within the cluster by Kubernetes services (ClusterIPs). This CIDR should not overlap with the VCN CIDR range. | string | "10.96.0.0/16" | no |
| sriov_cni_plugin_daemonset_url | The URL path to the manifest. Leave unset for tags of <a href=https://github.com/openshift/sriov-cni using sriov_cni_plugin_version. | string | null | no |
| sriov_cni_plugin_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "network" | no |
| sriov_cni_plugin_version | Version to install. Ignored when an explicit value for sriov_cni_plugin_daemonset_url is provided. | string | "master" | no |
| sriov_device_plugin_daemonset_url | The URL path to the manifest. Leave unset for tags of k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-network-device-plugin using sriov_device_plugin_version. | string | null | no |
| sriov_device_plugin_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "network" | no |
| sriov_device_plugin_version | Version to install. Ignored when an explicit value for sriov_device_plugin_daemonset_url is provided. | string | "master" | no |
| ssh_private_key | The contents of the SSH private key file, optionally base64-encoded. May be provided via SSH agent when unset. | string | null | no |
| ssh_private_key_path | A path on the local filesystem to the SSH private key. May be provided via SSH agent when unset. | string | null | no |
| ssh_public_key | The contents of the SSH public key file, optionally base64-encoded. Used to allow login for workers/bastion/operator with corresponding private key. | string | null | no |
| ssh_public_key_path | A path on the local filesystem to the SSH public key. Used to allow login for workers/bastion/operator with corresponding private key. | string | null | no |
| state_id | Optional Terraform state_id from an existing deployment of the module to re-use with created resources. | string | null | no |
| tag_namespace | The tag namespace for standard OKE defined tags. | string | "oke" | no |
| tenancy_id | The tenancy id of the OCI Cloud Account in which to create the resources. | string | null | no |
| tenancy_ocid | A tenancy OCID automatically populated by Resource Manager. | string | null | no |
| timezone | The preferred timezone for workers, operator, and bastion instances. | string | "Etc/UTC" | no |
| user_id | The id of the user that terraform will use to create the resources. | string | null | no |
| vcn_create_internet_gateway | Whether to create an internet gateway with the VCN. Defaults to automatic creation when public network resources are expected to utilize it. | string | "auto" | no |
| vcn_create_nat_gateway | Whether to create a NAT gateway with the VCN. Defaults to automatic creation when private network resources are expected to utilize it. | string | "auto" | no |
| vcn_create_service_gateway | Whether to create a service gateway with the VCN. Defaults to always created. | string | "always" | no |
| vcn_dns_label | A DNS label for the VCN, used in conjunction with the VNIC's hostname and subnet's DNS label to form a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for each VNIC within this subnet. Defaults to the generated Terraform 'state_id' value. | string | null | no |
| vcn_id | Optional ID of existing VCN. Takes priority over vcn_name filter. Ignored when create_vcn = true. | string | null | no |
| vcn_name | Display name for the created VCN. Defaults to 'oke' suffixed with the generated Terraform 'state_id' value. | string | null | no |
| whereabouts_daemonset_url | The URL path to the manifest. Leave unset for tags of k8snetworkplumbingwg/whereabouts using whereabouts_version. | string | null | no |
| whereabouts_namespace | Kubernetes namespace for deployed resources. | string | "default" | no |
| whereabouts_version | Version to install. Ignored when an explicit value for whereabouts_daemonset_url is provided. | string | "master" | no |
| worker_block_volume_type | Default block volume attachment type for Instance Configurations when unspecified on a pool. | string | "paravirtualized" | no |
| worker_capacity_reservation_id | The ID of the Compute capacity reservation the worker node will be launched under. See Capacity Reservations for more information. | string | null | no |
| worker_compartment_id | The compartment id where worker group resources will be created. | string | null | no |
| worker_image_id | Default image for worker pools when unspecified on a pool. | string | null | no |
| worker_image_os | Default worker image operating system name when worker_image_type = 'oke' or 'platform' and unspecified on a pool. | string | "Oracle Linux" | no |
| worker_image_os_version | Default worker image operating system version when worker_image_type = 'oke' or 'platform' and unspecified on a pool. | string | "8" | no |
| worker_image_type | Whether to use a platform, OKE, or custom image for worker nodes by default when unspecified on a pool. When custom is set, the worker_image_id must be specified. | string | "oke" | no |
| worker_pool_mode | Default management mode for workers when unspecified on a pool. | string | "node-pool" | no |
| worker_volume_kms_key_id | The ID of the OCI KMS key to be used as the master encryption key for Boot Volume and Block Volume encryption by default when unspecified on a pool. | string | null | no |
Inputs
Sub-modules currently use a sparse definition of inputs required from the root:
Identity Access Management (IAM)
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| create_iam_autoscaler_policy | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_cluster_policy | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_defined_tags | Tags | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_kms_policy | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_operator_policy | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_resources | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_tag_namespace | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_iam_worker_policy | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| enable_ipv6 | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| use_defined_tags | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| autoscaler_compartments | Policy | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| worker_compartments | n/a | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| defined_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| cluster_id | Common | string | n/a | yes |
| cluster_kms_key_id | KMS | string | n/a | yes |
| compartment_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| network_compartment_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| operator_volume_kms_key_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| policy_name | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| state_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| tag_namespace | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| tenancy_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| worker_volume_kms_key_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
Network
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| allow_rules_cp | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| allow_rules_internal_lb | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| allow_rules_pods | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| allow_rules_public_lb | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| allow_rules_workers | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| drg_attachments | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| allow_bastion_cluster_access | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| allow_node_port_access | Network | bool | n/a | yes |
| allow_pod_internet_access | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| allow_worker_internet_access | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| allow_worker_ssh_access | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| assign_dns | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| bastion_is_public | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| control_plane_is_public | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_bastion | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_cluster | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_internet_gateway | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_nat_gateway | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| create_operator | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| enable_ipv6 | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| enable_waf | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| use_defined_tags | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| use_stateless_rules | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| worker_is_public | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| vcn_cidrs | n/a | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| vcn_ipv6_cidrs | n/a | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| subnets | n/a | map(object({ create = optional(string) id = optional(string) newbits = optional(string) netnum = optional(string) cidr = optional(string) display_name = optional(string) dns_label = optional(string) ipv6_cidr = optional(string) })) | n/a | yes |
| nsgs | n/a | map(object({ create = optional(string) id = optional(string) })) | n/a | yes |
| defined_tags | Tags | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| bastion_allowed_cidrs | n/a | set(string) | n/a | yes |
| control_plane_allowed_cidrs | n/a | set(string) | n/a | yes |
| cni_type | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| compartment_id | Common | string | n/a | yes |
| ig_route_table_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| igw_ngw_mixed_route_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| internet_gateway_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| load_balancers | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| nat_gateway_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| nat_route_table_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| state_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| tag_namespace | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| vcn_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
Bastion
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| assign_dns | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| is_public | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| upgrade | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| use_defined_tags | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| nsg_ids | n/a | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| shape | n/a | map(any) | n/a | yes |
| defined_tags | Tags | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| availability_domain | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| await_cloudinit | Bastion | string | n/a | yes |
| bastion_image_os_version | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| compartment_id | Common | string | n/a | yes |
| image_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| ssh_private_key | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| ssh_public_key | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| state_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| subnet_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| tag_namespace | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| timezone | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| user | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| volume_kms_key_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
Cluster
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oidc_token_authentication_config | n/a | any | n/a | yes |
| assign_public_ip_to_control_plane | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| control_plane_is_public | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| oidc_discovery_enabled | OIDC | bool | n/a | yes |
| oidc_token_auth_enabled | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| use_signed_images | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| ip_families | n/a | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| cluster_defined_tags | Tagging | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| cluster_freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| persistent_volume_defined_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| persistent_volume_freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| service_lb_defined_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| service_lb_freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| backend_nsg_ids | n/a | set(string) | n/a | yes |
| control_plane_nsg_ids | n/a | set(string) | n/a | yes |
| image_signing_keys | n/a | set(string) | n/a | yes |
| cluster_kms_key_id | Cluster | string | n/a | yes |
| cluster_name | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| cluster_type | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| cni_type | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| compartment_id | Common | string | n/a | yes |
| control_plane_subnet_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| kubernetes_version | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| pods_cidr | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| service_lb_subnet_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| services_cidr | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| state_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| tag_namespace | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| use_defined_tags | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| vcn_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
Workers
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| image_ids | Map of images for filtering with image_os and image_os_version. | any | {} | no |
| indexed_images | Map of images. | any | {} | no |
| worker_pools | Tuple of OKE worker pools where each key maps to the OCID of an OCI resource, and value contains its definition. | any | {} | no |
| allow_short_container_image_names | Whether to allow short container image names for K8s version >= 1.34.0. See CRI-O pull request for more information. | bool | false | no |
| assign_dns | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| assign_public_ip | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| disable_default_cloud_init | Whether to disable the default OKE cloud init and only use the cloud init explicitly passed to the worker pool in 'worker_cloud_init'. | bool | false | no |
| enable_ipv6 | Whether to create a dual-stack (IPv4/IPv6) cluster. | bool | false | no |
| legacy_imds_endpoints_disabled | Whether to disable requests to the IMDSv1 endpoint and only allow requests to the IMDSv2 endpoint. See Instance Metadata for more information. | bool | false | no |
| pv_transit_encryption | Whether to enable in-transit encryption for the data volume's paravirtualized attachment by default when unspecified on a pool. | bool | false | no |
| use_defined_tags | Whether to apply defined tags to created resources for IAM policy and tracking. | bool | false | no |
| cloud_init | List of maps containing cloud init MIME part configuration for worker nodes. Merged with pool-specific definitions. See https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/template/latest/docs/data-sources/cloudinit_config.html#part for expected schema of each element. | list(map(string)) | [] | no |
| ad_numbers | n/a | list(number) | n/a | yes |
| pod_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security group (NSG) IDs for pod security. Combined with 'pod_nsg_ids' specified on each pool. | list(string) | [] | no |
| worker_nsg_ids | An additional list of network security group (NSG) IDs for node security. Combined with 'nsg_ids' specified on each pool. | list(string) | [] | no |
| compute_clusters | Whether to create compute clusters shared by nodes across multiple worker pools enabled for 'compute-cluster'. | map(any) | {} | no |
| preemptible_config | Default preemptible Compute configuration when unspecified on a pool. See Preemptible Worker Nodes for more information. | map(any) | { "enable": false, "is_preserve_boot_volume": false } | no |
| shape | Default shape of the created worker instance when unspecified on a pool. | map(any) | { "boot_volume_size": 50, "memory": 16, "ocpus": 2, "shape": "VM.Standard.E4.Flex" } | no |
| ad_numbers_to_names | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| defined_tags | Defined tags to be applied to created resources. Must already exist in the tenancy. | map(string) | {} | no |
| freeform_tags | Freeform tags to be applied to created resources. | map(string) | {} | no |
| node_labels | Default worker node labels. Merged with labels defined on each pool. | map(string) | {} | no |
| node_metadata | Map of additional worker node instance metadata. Merged with metadata defined on each pool. | map(string) | {} | no |
| max_pods_per_node | The default maximum number of pods to deploy per node when unspecified on a pool. Absolute maximum is 110. Ignored when when cni_type != 'npn'. | number | 31 | no |
| worker_pool_size | Default size for worker pools when unspecified on a pool. | number | 0 | no |
| agent_config | Default agent_config for self-managed worker pools created with mode: 'instance', 'instance-pool', or 'cluster-network'. See InstanceConfig for more information. | object({ are_all_plugins_disabled = bool, is_management_disabled = bool, is_monitoring_disabled = bool, plugins_config = map(string), }) | n/a | yes |
| platform_config | Default platform_config for self-managed worker pools created with mode: 'instance', 'instance-pool', or 'cluster-network'. See PlatformConfig for more information. | object({ type = optional(string), are_virtual_instructions_enabled = optional(bool), is_access_control_service_enabled = optional(bool), is_input_output_memory_management_unit_enabled = optional(bool), is_measured_boot_enabled = optional(bool), is_memory_encryption_enabled = optional(bool), is_secure_boot_enabled = optional(bool), is_symmetric_multi_threading_enabled = optional(bool), is_trusted_platform_module_enabled = optional(bool), numa_nodes_per_socket = optional(number), percentage_of_cores_enabled = optional(bool), }) | null | no |
| apiserver_private_host | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| block_volume_type | Default block volume attachment type for Instance Configurations when unspecified on a pool. | string | "paravirtualized" | no |
| capacity_reservation_id | The ID of the Compute capacity reservation the worker node will be launched under. See Capacity Reservations for more information. | string | null | no |
| cluster_ca_cert | Base64+PEM-encoded cluster CA certificate for unmanaged instance pools. Determined automatically when 'create_cluster' = true or 'cluster_id' is provided. | string | null | no |
| cluster_dns | Cluster DNS resolver IP address. Determined automatically when not set (recommended). | string | null | no |
| cluster_id | An existing OKE cluster OCID when create_cluster = false. | string | null | no |
| cluster_type | The cluster type. See Working with Enhanced Clusters and Basic Clusters for more information. | string | "basic" | no |
| cni_type | The CNI for the cluster: 'flannel' or 'npn'. See Pod Networking. | string | "flannel" | no |
| compartment_id | The compartment id where resources will be created. | string | null | no |
| image_id | Default image for worker pools when unspecified on a pool. | string | null | no |
| image_os | Default worker image operating system name when worker_image_type = 'oke' or 'platform' and unspecified on a pool. | string | "Oracle Linux" | no |
| image_os_version | Default worker image operating system version when worker_image_type = 'oke' or 'platform' and unspecified on a pool. | string | "8" | no |
| image_type | Whether to use a platform, OKE, or custom image for worker nodes by default when unspecified on a pool. When custom is set, the worker_image_id must be specified. | string | "oke" | no |
| kubeproxy_mode | The mode in which to run kube-proxy when unspecified on a pool. | string | "iptables" | no |
| kubernetes_version | The version of Kubernetes used for worker nodes. | string | "v1.26.2" | no |
| pod_subnet_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| ssh_public_key | The contents of the SSH public key file. Used to allow login for workers/bastion/operator with corresponding private key. | string | null | no |
| state_id | Optional Terraform state_id from an existing deployment of the module to re-use with created resources. | string | null | no |
| tag_namespace | The tag namespace for standard OKE defined tags. | string | "oke" | no |
| tenancy_id | The tenancy id of the OCI Cloud Account in which to create the resources. | string | null | no |
| timezone | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| volume_kms_key_id | The ID of the OCI KMS key to be used as the master encryption key for Boot Volume and Block Volume encryption by default when unspecified on a pool. | string | null | no |
| worker_pool_mode | Default management mode for workers when unspecified on a pool. Only 'node-pool' is currently supported. | string | "node-pool" | no |
| worker_subnet_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
Operator
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| assign_dns | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_cilium | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_helm | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_helm_from_repo | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_istioctl | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_k8sgpt | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_k9s | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_kubectl_from_repo | n/a | bool | true | no |
| install_kubectx | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_oci_cli_from_repo | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| install_stern | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| pv_transit_encryption | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| upgrade | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| use_defined_tags | n/a | bool | n/a | yes |
| cloud_init | n/a | list(map(string)) | n/a | yes |
| nsg_ids | n/a | list(string) | n/a | yes |
| shape | n/a | map(any) | n/a | yes |
| defined_tags | Tags | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| freeform_tags | n/a | map(string) | n/a | yes |
| availability_domain | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| await_cloudinit | Operator | string | n/a | yes |
| bastion_host | Bastion (to await cloud-init completion) | string | n/a | yes |
| bastion_user | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| compartment_id | Common | string | n/a | yes |
| image_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| kubeconfig | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| kubernetes_version | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| operator_image_os_version | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| ssh_private_key | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| ssh_public_key | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| state_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| subnet_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| tag_namespace | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| timezone | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| user | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
| volume_kms_key_id | n/a | string | n/a | yes |
Outputs
Identity Access Management (IAM)
dynamic_group_idsCluster IAM dynamic group IDspolicy_statementsCluster IAM policy statements
Network
bastion_nsg_idbastion_subnet_cidrbastion_subnet_idReturn configured/created subnet IDs and CIDRs when applicablecontrol_plane_nsg_idcontrol_plane_subnet_cidrcontrol_plane_subnet_idfss_nsg_idfss_subnet_cidrfss_subnet_idint_lb_nsg_idint_lb_subnet_cidrint_lb_subnet_idnetwork_security_rulesnsg_idsoperator_nsg_idoperator_subnet_cidroperator_subnet_idpod_nsg_idpod_subnet_cidrpod_subnet_idpub_lb_nsg_idpub_lb_subnet_cidrpub_lb_subnet_idworker_nsg_idworker_subnet_cidrworker_subnet_id
Bastion
idpublic_ip
Cluster
cluster_idendpointsoidc_discovery_endpoint
Workers
worker_count_expected# of nodes expected from created worker poolsworker_drain_expected# of nodes expected to be draining in worker poolsworker_instancesCreated worker pools (mode == 'instance')worker_pool_autoscale_expected# of worker pools expected with autoscale enabled from created worker poolsworker_pool_idsCreated worker pool IDsworker_pool_ipsCreated worker instance private IPs by pool for available modes ('node-pool', 'instance').worker_poolsCreated worker pools (mode != 'instance')
Operator
idprivate_ip
Resources
Identity Access Management (IAM)
- oci_identity_dynamic_group.autoscaling
- oci_identity_dynamic_group.cluster
- oci_identity_dynamic_group.operator
- oci_identity_dynamic_group.workers
- oci_identity_policy.cluster
- oci_identity_policy.networking_policies
- oci_identity_tag.oke
- oci_identity_tag_namespace.oke
- time_sleep.await_iam_resources
Network
- null_resource.validate_subnets
- oci_core_drg.oke
- oci_core_drg_attachment.extra
- oci_core_drg_attachment.oke
- oci_core_network_security_group.bastion
- oci_core_network_security_group.cp
- oci_core_network_security_group.fss
- oci_core_network_security_group.int_lb
- oci_core_network_security_group.operator
- oci_core_network_security_group.pods
- oci_core_network_security_group.pub_lb
- oci_core_network_security_group.workers
- oci_core_network_security_group_security_rule.oke
- oci_core_route_table.igw_ngw_mixed_route_id
- oci_core_security_list.oke
- oci_core_subnet.oke
Bastion
Cluster
Workers
- oci_containerengine_node_pool.autoscaled_workers
- oci_containerengine_node_pool.tfscaled_workers
- oci_containerengine_virtual_node_pool.workers
- oci_core_cluster_network.workers
- oci_core_compute_cluster.shared
- oci_core_compute_cluster.workers
- oci_core_instance.compute_cluster_workers
- oci_core_instance.workers
- oci_core_instance_configuration.workers
- oci_core_instance_pool.autoscaled_workers
- oci_core_instance_pool.tfscaled_workers
Operator
Version 5.x
Summary
- Improved config flexibility, e.g.:
- All resources in same tfstate
- Identity resources only/enabled individually
- Network resources only/enabled individually
- Cluster with existing network VCN/subnets/NSGs
- Cluster & isolated NSGs with existing network VCN/subnets
- Workers with existing cluster/network
- Workers with tag-based group/policy for Cluster Autoscaler, ...
- Operator with existing cluster & group/policy for cluster access
- Workers: resource type configuration (Self-Managed, Virtual)
mode="node-pool"- New
mode="virtual-node-pool" - New
mode="instance" - New
mode="instance-pool" - New
mode="cluster-network"
- Workers: merge/override global & pool-specific for most inputs
- Network: Referential NSG security rule definitions
- Sub-module refactor
iam: Dynamic groups, policies, defined tagsnetwork: VCN, subnets, NSGs, DRGsbastion: Bastion host for external VCN accesscluster: OKE managed Kubernetes clusterworkers: Compute pools for cluster workloads with configurable resource typesoperator: Operator instance with access to the OKE cluster endpointutilities: Additional automation for cluster operations performed by the moduleextensions: Optional cluster software for evaluation
Status
Pre-release / Beta
Core features of the module are working.
Some features under utilities need re-implementation/testing:
- OCIR
- Worker pool
drain
Documentation in progress.
Breaking changes
- Input variables
- Pending
Migration
Pending
Version 4.x
Summary
- ...?
Status
Released
This is the latest supported version of the module.
Migration
Pending
Version 3.x
Summary
Status
Maintenance
Migration
Pending
Version 2.x
Status
Maintenance
Version 1.x
Status
Unsupported
Coding conventions
This project adheres to the following conventions:
- Module structure
- Adopting the right case type
- Good names for files and Terraform objects (resources, variables, outputs)
New conventions may be added to the list in future. All contributions should adhere to the list as published when the contribution is made.
Use PR comments and the GitHub suggestion feature to agree on the final result.
Module Structure
- This project adheres to the {uri-terraform-standard-module-structure}[Terraform Standard Module Structure]
- Any nested module calls are in the appropriate
module-<name>.tffile at the root of the project. - All variables declarations must be in
variables.tforvariables-<group>.tf - All ouputs declarations must be in
outputs.tf,outputs-<group>.tf, or colocated with their values. - All variables and outputs must have descriptions.
- Nested modules must exist under the
modulessubdirectory. - Examples of how to use the module must be placed in the
examplessubdirectory, with documentation underdocs.
Documentation format
This project uses Markdown with the *.md file extension.
HashiCorp Terraform Registry
- README files must be in Markdown format
- All links must use absolute path, relative links are not supported
Terraform code
Case type, Files, Names
- Use
snake_casewhen naming Terraform files, variables and resources - If you need a new .tf file for better clarity, use this naming scheme:
<resources_group>: e.g.subnets.tf,nsgs.tf - If your variable is controlling a behaviour, use imperative style to name it: e.g.
create_internet_gateway,use_cluster_encryption
Formatting
The following should be performed as needed before committing changes:
- Run
terraform fmt -recursivefrom the project root directory. - Run
tflint --recursivefrom the project root directory (see documentation here) and address new warnings.
Variable blocks
Variables should always be in the format below:
variable "xyz" {
default = "A default value"
description: "Add (Updatable) at the begining of the description if this value do not triggers a resource recreate"
type: string
Variables exposed by the root module:
- must be included with its default value in the approriate tfvars example file.
- must define a default value that matches its type and will not alter existing behavior of the module.
- must define a description that describes how changes to the value will impact resources and interact with other variables when applicable.
- should be prefixed with the name of the component they pertain to unless shared across more than one, e.g.
worker_,operator_, etc. - should use imperative verbs when controlling behavior, e.g.
create,use, etc. - should include preconditions for input validation where possible.
- should prefer
nullfor empty/unset defaults over empty string or other values.
Variables within submodules:
- must define only a type matching that of the root module.
- must omit defaults to ensure they are referenced from the root module.
- must omit descriptions to avoid maintaining in multiple places.
- should match the name of their root module counterparts, with the possible exception of a component prefix when redundant and unambiguous, e.g.
worker_,operator_, etc.
Do not hesitate to insert a brief comment in the variable block if it helps to clarify your intention.
WARNING: No default value for compartment_id or any other variables related to provider authentication in module or examples files. The user will have to explicitly set these values.
Examples
Examples should promote good practices as much as possible e.g. avoid creating resources in the tenancy root compartment. Please review the OCI Security Guide.
Coding conventions
This project adheres to the following conventions:
- Module structure
- Adopting the right case type
- Good names for files and Terraform objects (resources, variables, outputs)
New conventions may be added to the list in future. All contributions should adhere to the list as published when the contribution is made.
Use PR comments and the GitHub suggestion feature to agree on the final result.
Module Structure
- This project adheres to the {uri-terraform-standard-module-structure}[Terraform Standard Module Structure]
- Any nested module calls are in the appropriate
module-<name>.tffile at the root of the project. - All variables declarations must be in
variables.tforvariables-<group>.tf - All ouputs declarations must be in
outputs.tf,outputs-<group>.tf, or colocated with their values. - All variables and outputs must have descriptions.
- Nested modules must exist under the
modulessubdirectory. - Examples of how to use the module must be placed in the
examplessubdirectory, with documentation underdocs.
Documentation format
This project uses Markdown with the *.md file extension.
HashiCorp Terraform Registry
- README files must be in Markdown format
- All links must use absolute path, relative links are not supported
Terraform code
Case type, Files, Names
- Use
snake_casewhen naming Terraform files, variables and resources - If you need a new .tf file for better clarity, use this naming scheme:
<resources_group>: e.g.subnets.tf,nsgs.tf - If your variable is controlling a behaviour, use imperative style to name it: e.g.
create_internet_gateway,use_cluster_encryption
Formatting
The following should be performed as needed before committing changes:
- Run
terraform fmt -recursivefrom the project root directory. - Run
tflint --recursivefrom the project root directory (see documentation here) and address new warnings.
Variable blocks
Variables should always be in the format below:
variable "xyz" {
default = "A default value"
description: "Add (Updatable) at the begining of the description if this value do not triggers a resource recreate"
type: string
Variables exposed by the root module:
- must be included with its default value in the approriate tfvars example file.
- must define a default value that matches its type and will not alter existing behavior of the module.
- must define a description that describes how changes to the value will impact resources and interact with other variables when applicable.
- should be prefixed with the name of the component they pertain to unless shared across more than one, e.g.
worker_,operator_, etc. - should use imperative verbs when controlling behavior, e.g.
create,use, etc. - should include preconditions for input validation where possible.
- should prefer
nullfor empty/unset defaults over empty string or other values.
Variables within submodules:
- must define only a type matching that of the root module.
- must omit defaults to ensure they are referenced from the root module.
- must omit descriptions to avoid maintaining in multiple places.
- should match the name of their root module counterparts, with the possible exception of a component prefix when redundant and unambiguous, e.g.
worker_,operator_, etc.
Do not hesitate to insert a brief comment in the variable block if it helps to clarify your intention.
WARNING: No default value for compartment_id or any other variables related to provider authentication in module or examples files. The user will have to explicitly set these values.
Examples
Examples should promote good practices as much as possible e.g. avoid creating resources in the tenancy root compartment. Please review the OCI Security Guide.
